
- Гідрологія і Гідрометрія
- Господарське право
- Економіка будівництва
- Економіка природокористування
- Економічна теорія
- Земельне право
- Історія України
- Кримінально виконавче право
- Медична радіологія
- Методи аналізу
- Міжнародне приватне право
- Міжнародний маркетинг
- Основи екології
- Предмет Політологія
- Соціальне страхування
- Технічні засоби організації дорожнього руху
- Товарознавство продовольчих товарів
Тлумачний словник
Авто
Автоматизація
Архітектура
Астрономія
Аудит
Біологія
Будівництво
Бухгалтерія
Винахідництво
Виробництво
Військова справа
Генетика
Географія
Геологія
Господарство
Держава
Дім
Екологія
Економетрика
Економіка
Електроніка
Журналістика та ЗМІ
Зв'язок
Іноземні мови
Інформатика
Історія
Комп'ютери
Креслення
Кулінарія
Культура
Лексикологія
Література
Логіка
Маркетинг
Математика
Машинобудування
Медицина
Менеджмент
Метали і Зварювання
Механіка
Мистецтво
Музика
Населення
Освіта
Охорона безпеки життя
Охорона Праці
Педагогіка
Політика
Право
Програмування
Промисловість
Психологія
Радіо
Регилия
Соціологія
Спорт
Стандартизація
Технології
Торгівля
Туризм
Фізика
Фізіологія
Філософія
Фінанси
Хімія
Юриспунденкция
On the photomicrograph of the inner flask of Vater-Pacini corpuscle one can see neuronal process. What process and of what type of neurocyte is that?
a. axon of multipolar neuron
b. axon of pseudounipolar neuron
c. +dendrite of pseudounipolar neuron
d. dendrite of multipolar neuron
e. axon of unipolar neuron
277. Sensory nerve ending that is responsible for temperature sense:
a. Vater-Pacini corpuiscle
b. Meissner’s corpuscle
c. neuromuscular spindle
d. +free nerve ending
e. Ruffini’s corpuscle
278. Nerve cells that form reflex arc:
a.+afferent, intercalary and efferent
b. afferent and intercalary
c. intercalary and efferent
d. afferent
e. efferent
279. Olfactory mucosa of the nasal cavity contains the following cells:
a. +sensory
b. endocrine
c. ciliated
d. goblet
e. neurosecretory
280. Sense organ whose sensory cells have a short dendrite and a long axon; the dendrites end in a thickening (called the rod or knob); each axon passes into the subjacent connective tissue where it forms one fibre of the olfactory nerve:
a. organ of hearing
b. organ of taste
c. organ of equilibrium
d. +organ of smell
e. organ of sight
281. Cells of olfactory organ:
a. ciliated
b. +sensory,supporting and basal
c. neurosecretory
d. goblet
e. endocrine
282. Cells that respond to angular acceleration:
a. cells of saccular macula
b. cells of urticular macula
c. +cells of ampullary crest
d. cells of spiral organ
e. cells of retina
283. Receptor cells, the dysfunction of which, causes disorder in appreciation of information about angular movements of the head:
a. hair cells of spiral organ
b. receptor cells of olfactory organ
c. rods and cones of retina
d. receptor gustatory cells
e. +hair cells of saccular and utricular maculae, and hair calls of ampullary crests
284. Otholithic membrane is situated in:
a. ampullary crest
b. spiral organ
c. +saccular and utricular maculae
d. vascular stria of cochlear duct of membranaceous labyrinth
e. spiral ligament
285. Sense organ, the receptor and supporting cells of which are surrounded by gelatinous cupula that is devoid of cavity:
a. +organ of equilibrium
b. organ of hearing
c. organ of smell
d. organ of taste
e. organ of vision
286. Cells that make up saccular and utricular maculae:
a. goblet cells
b. +hair cells and supporting cells
c. nerve cells
d. nonciliated cells and basal cells
e. columnar cells and intercalated cells
287. Cells of the organ of equilibrium, on the apical pole of which, there are sixty to eighty stereiocilia (nonmotile microvilli) and one kinocilium (motile cytoplasmic filament):
a. supporting cells
b. squamous epithelial cells
c. cuboidal epithelial cells
d. cylindrical epithelial cells
e. +hair sensory cells
288. Sense organ, sensory and supporting cells of which, are covered by gelatinous otolithic membrane containing otoliths (crystals of calcium carbonate):
a. +organ of equilibrium
b. organ of hearing
c. organ of smell
d. organ of taste
e. organ of sight
289. Which of the following cells are the part of saccule and utricle of the organ of equilibrium:
a. basal cells and non-ciliated cells
b. ciliated cells
c. goblet cells
d. +hair cells and supporting cells
e. endocrine cells
290. Sense organ, hair cells and supporting cells of which, are covered by otolithic membrane:
a. organ of sight
b. organ of hearing
c. organ of smell
d. +organ of equilibrium
e. organ of taste
291. Hair sensory cells of the macula of utricle in the vestibular part of membranaceous labyrinth respond to:
a. electromagnetic waves
b. +linear acceleration
c. angular acceleration
d. vibration
e. sound waves
292. Bodies of retinal glyocytes are situated in:
a. layer of ganglion cells
b. external nuclear layer
c.+inner nuclear layer
d. inner plexiform layer
e. external plexiform layer
293. External plexiform layer of the retina contains:
a. bodies of photoreceptor cells
b. peripheral processes of photoreceptor cells
c. bodies of bipolar neurons
d. +synaptic contacts of photoreceptor cells with dendrites of bipolar neurons and processes of horizontal neurons
e. axons of bipolar neurons, dendrites of ganglion cells and processes of amacrine cells
294. Inner plexiform layer of the retina contains:
a. bodies of photoreceptor cells
b. peripheral processes of photoreceptor cells
c. bodies of bipolar neurons
d. synaptic contacts of photoreceptor cells with dendrites of bipolar neurons and processes of horizontal neurons
e. +axons of bipolar neurons, dendrites of ganglion cells and processes of amacrine cells
295. Shape of the cells of retinal pigment epithelium in transverse section:
a. +mainly hexagonal
b. triangular
c. round
d. oval
e. stellate
296. Retinal bipolar neurons transmit nerve impulse to the following cells:
a. horizontal
b. pigment
c. photoreceptor
d. glia fibre-like supporting
e. +ganglionic
297. Axons of the retinal photoreceptor cells form contacts with the following cells:
a. pigment
b. +bipolar
c. amacrine
d. ganglion
e. glia fibre-like supporting
298. Retinal bipolar neurons connect the following cells:
a.+photoreceptor and ganglion
b. pigment and horizontal
c. photoreceptor and pigment
d. amacrine and pigment
e. ganglion and pigment
299. Retinal horizontal neurons connect the following cells:
a. +photoreceptor
b. pigment and photoreceptor
c. pigment and amacrine
d. ganglion and amacrine
e. pigment and glia fibre-like supporting
300. Retinal amacrine neurons connect the following cells:
a. +ganglion
b. pigment and photoreceptor
c. ganglion and horizontal
d. pigment and glia fibre-like supporting
e. pigment
301. Part of the rod photoreceptor cell that contains visual pigment rhodopsin:
a. +outer segment of the rod
b. inner segment of the rod
c. cilium
d. cytoplasm of the cell body
e. rod process
302. Part of the cone photoreceptor cell that contains visual pigment iodopsin:
a. inner segment of the cone
b. +outer segment of the cone
c. cilium
d. cytoplasm of the cell body
e. cone process
303. Part of the cone photoreceptor cell that contains ellipsoid:
a. outer segment of the cone
b.+inner segment of the cone
c. cilium
d. cytoplasm of the cell body
e. cone process
304. Part of the rod photoreceptor cell that contains basal corpuscle connected with nine pairs of peripheral microtubules and one pair of central microtubules:
a. +inner segment of the rod
b. outer segment of the rod
c. cilium
d. cytoplasm of the cell body
e. rod process
305. Epithelium that lines the anterior surface of lens:
a. +simple squamous
b. birowed
c. pseudostratified ciliated
d. stratified squamous non-keratinized
e. stratified squamous keratinized
306. Retinal layer that consists of single row of high, mainly hexagonal cells containing melanosomes:
a. external nuclear layer
b. external plexiform layer
c. +pigment cell layer
d. inner nuclear layer
e. inner plexiform layer
307. Retinal cell, outer segment of the process of which, contains visual pigment rhodopsin:
a. +rod
b. cone
c. bipolar cell
d. amacrine cell
e. ganglion cell
308. Retinal cell, outer segment of the process of which, contains visual pigment iodopsin:
a. rod
b. +cone
c. bipolar cell
d. amacrine cell
e. ganglion cell
309. Retinal layer of rods and cones is formed by processes of:
a. +photoreceptor cells
b. bipolar neurons
c. ganglion cells
d. horizontal neurons
e. radiate glial cells
310. Cells, the bodies of which form external nuclear layer;
a. bipolar neurons
b. horizontal neurons
c. amacrine neurons
d. ganglion cells
e. +photoreceptor cells
311. Cells, the bodies of which, form retinal layer of ganglion cells:
a. photoreceptor cells
b. bipolar neurons
c. horizontal neurons
d. +ganglion cells
e. amacrine neurons
312. Cells, the processes of which, make up the external and internal limiting membranes of the retina:
a. bipolar neurons
b. horizontal neurons
c. ganglion cells
d. +radial gliocytes
e. neurosensory cells
313. Retinal layer that consists of the bodies of photoreceptor cells:
a. layer of rods and cones
b. +external nuclear layer
c. inner nuclear layer
d. layer of ganglion cells
e. inner plexiform layer
314. Retinal layer, that consists of processes of photoreceptor cells:
a. +layer of rods and cones
b. external nuclear layer
c. external plexiform layer
d. inner plexiform layer
e. layer of optic nerve fibres
315. Retinal layer that consists of the bodies of bipolar, horintal and amacrine neurons:
a. external nuclear layer
b. +inner nuclear layer
c. layer of ganglion cells
d. layer of rods and cones
e. inner plexiform layer
316. Sclera is made up of:
a. reticular tissue
b. dense irregular fibrous connective tissue
c. +dense regular fibrous connective tissue
d. loose irregular fibrous connective tissue
e. adipose tissue
317. Corneal layer that consists of stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium:
a. +anterior epithelium
b. anterior limiting lamina
c. substantia propria
d. posterior limiting lamina
e. posterior epithelium
318. Corneal layer that consists of simple squamous epithelium:
a. anterior epithelium
b. anterior limiting lamina
c. substantia propria
d. posterior limiting lamina
e. +posterior epithelium
319. Corneal posterior epithelium is:
a. +simple squamous
b. pseudostratified ciliated
c. stratified squamous keratinized
d. stratified squamous non-keratinized
e. transitional
320. Retinal layer of optic nerve fibres is made up of:
a. dendrites of bipolar neurons
b. axons of horizontal neurons
c. +axons of ganglion cells
d. dendrites of amacrine neurons
e. processes of radial gliocytes
321. Epithelium lining internal surface of tympanic membrane:
a. +simple squamous
b. stratified squamous non-keratinized
c. stratified squamous keratinized
d. pseudostratified ciliated
e. transitional
322. Cavity of the cochlear duct of membranous labyrinth is filled by:
a. lymph
b. perilymph
c. +endolymph
d. air
e. blood
323. Cavity of the vestibular part of membranous labyrinth is filled by:
a. lymph
b. perilymph
c. +endolymph
d. air
e. blood
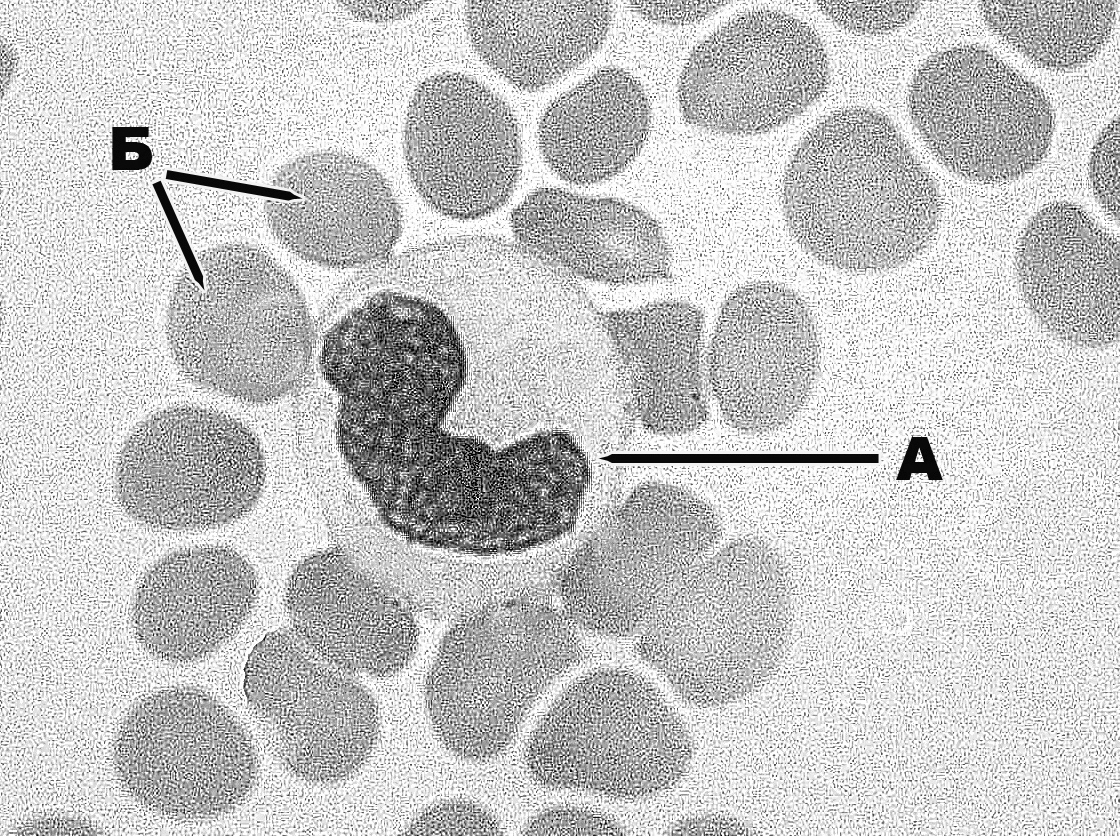
324. Outer hair cells of the spiral organ of Corti rest on the following cells:
a. +outer phalangeal cells
b. outer rod (pillar) cells
c. Hensen’s cells
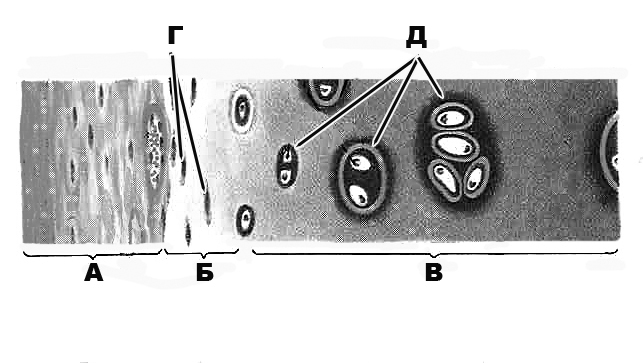
d. Claudius’ cells
e. supporting cells
325. Outer hair cells are characterized by the fact that:
a. their stereocilia are not attached to the tectorial membrane
b. they are pyriform in shape
c. their agranular endoplasmic reticulum is poorly developed
d. they rest on basal membrane
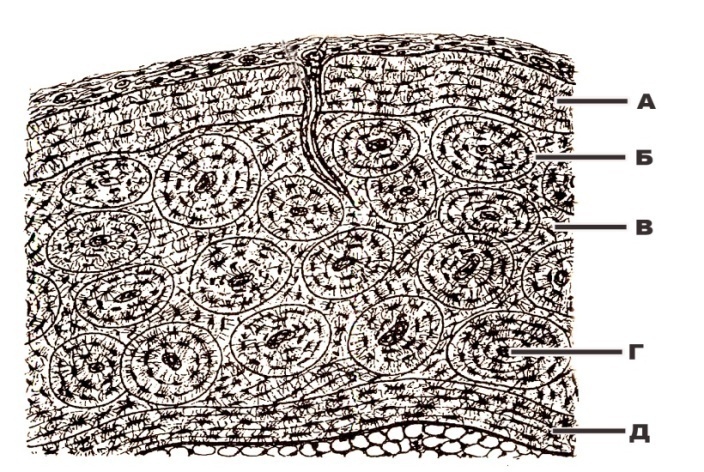
e. +they are innervated mainly by efferent nerve fibres
326. Inner hair cells are characterized by the fact that:
a. they are arranged in several rows
b. they are cylindrical in shape
c. they contain well developed agranular endoplasmic reticulum, forming cisternae
d. they rest on basal membrane
e.+ they are innervated mainly by sensory nerves
327. Columnar epitheliocytes of the spiral organ, that (on their apical pole) contain thirty to sixty stereocilia arranged in three to four rows:
a. inner phalangeal cells
b. outer phalangeal cells
c. +inner hair cells
d. outer hair cells
e. outer rod (pillar) cells
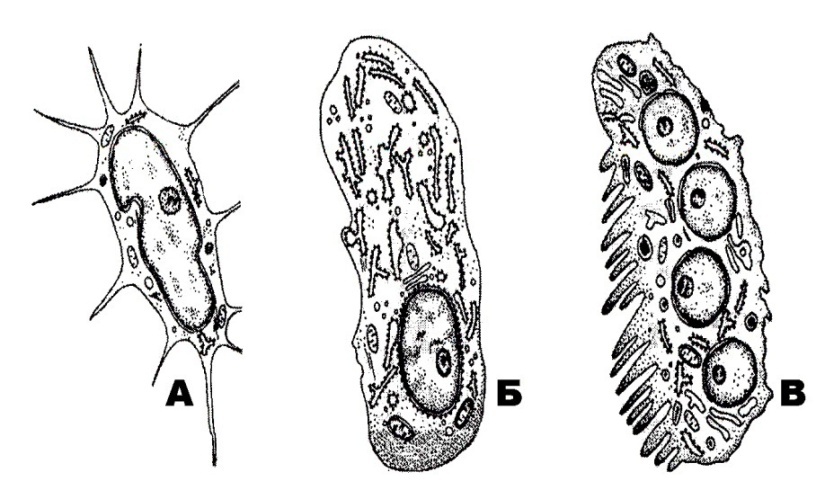
328. Epitheliocytes of the spiral organ that form tunnel of Corti:
a. inner and outer hair cells
b. inner phalangeal and inner rod cells
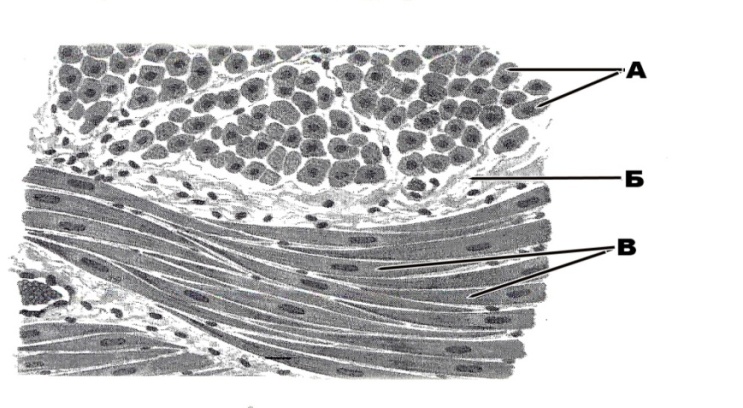
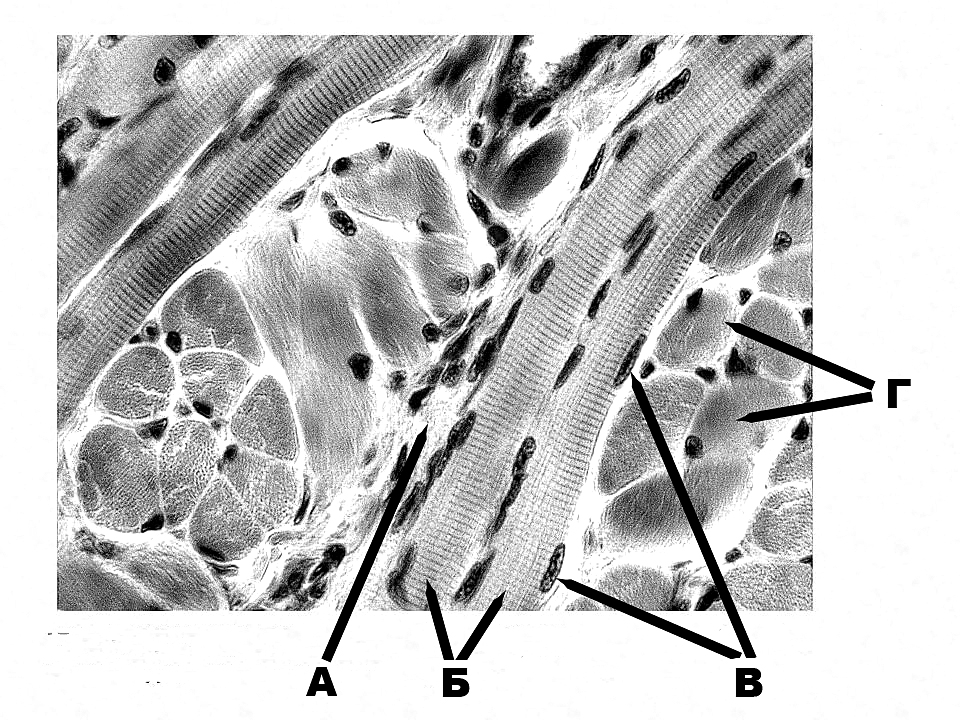
c. outer rod and outer phalangeal cells
d. cells of Hensen and cells of Claudius
e. +inner rod and outer rod cells
329. The first sensory neuron of auditory tract is situated in:
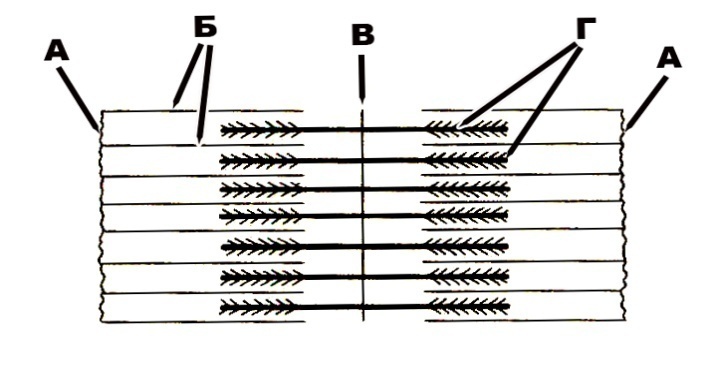
a. vestibular nucleus of the medulla oblongata
b. quadrigeminal plate
c. thalamic region
d. spiral organ
e. +spiral ganglion
On the electron photomicrograph of the spiral organ one can see some jug-shaped cells. The cells are arranged in one row, and they contain stereocilia on their apical pole. What cells are these?
a. outer and inner rod cells
b. outer phalangeal cells
c. outer hair cells
d. inner phalangeal cells
e. +inner hair cells
331. Cylindrical sensory epithelial cells that are arranged in three to four rows within the spiral organ:
a. inner and outer rod cells
b. outer palangeal cells
c. inner phalangeal cells
d. inner hair cells
e. +outer hair cells
332. Cells that make up taste buds:
a. goblet (flask) cells
b. ciliated cells
c. nerve cells
d. +receptor, supporting and basal cells
e. rod and cilia-free cells
|
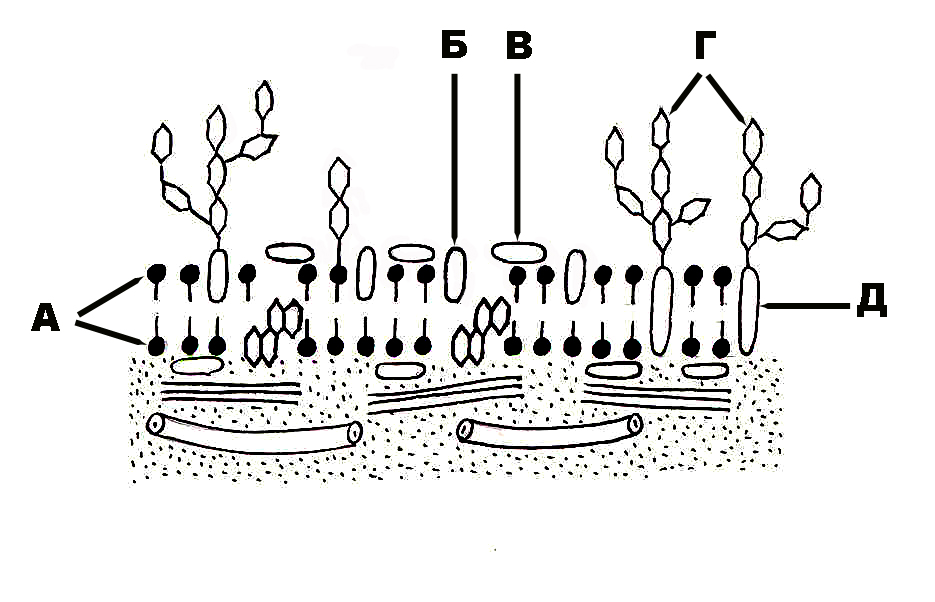
333. Structure of the plasmalemma that is designated with the letter A:
a. molecules of the oligosaccharides
b. membrane proteins
c. half-integral proteins
d. integral proteins
e. +double layer of lipid molecules
334. Structure of the plasmolemma that is designated with the letter Б:
a. molecules of the oligosaccharides
b. membrane proteins
c. +half-integral prtoteins
d. integral proteins
e. double layer of lipid molecules
335. Structure of the plasmalemma that is designated with the letter B:
a. molecules of oligosaccharides
b. +membrane proteins
c. half-integral proteins
d. integral proteins
e. double layer of lipid molecules
336. Structure of the plasmalemma that is designated with the letter Г:
a.+molecules of oligosaccharides
b. membrane proteins
c. half-integral proteins
d. integral proteins
c. double layer of lipid molecules
337. Structure of the plasmalemma that is designated with the letter Д:
a. molecules of oligosaccharides
b. membrane proteins
c. half-integral proteins
d. +integral proteins
e. double layer of lipid molecules

|
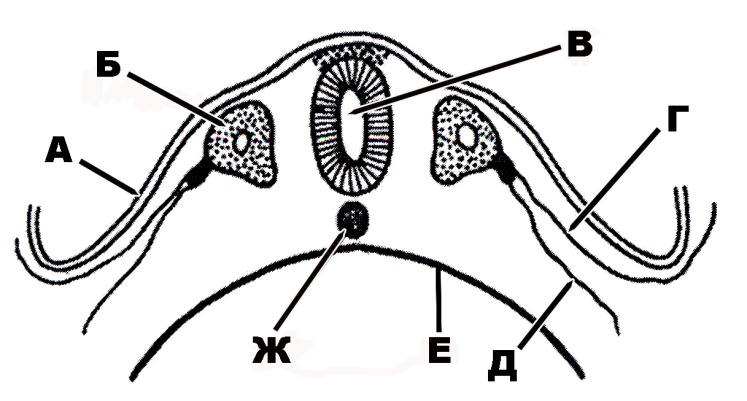
338. Phase of mitosis that is designated with the letter A:
a. telophase
b. metaphase
c. anaphase
d. prophase
e. +interphase
339. Phase of mitosis that is designated with the letter Б:
a. telophase
b. metaphase
c. anaphase
d. +prophase
e. interphase
340. Phase of mitosis that is designated with the letter B:
a. telophase
b. +metaphase
c. anaphase
d. prophase
e. interphase
341. Phase of mitosis that is designated with the letter Г:
a. telophase
b. metaphase
c. +anaphase
d. prophase
e. interphase
342. Phase of mitosis that is designated with the letter Д:
a. +telophase
b. metaphase
c. anaphase
d. prophase
e. interphase
|
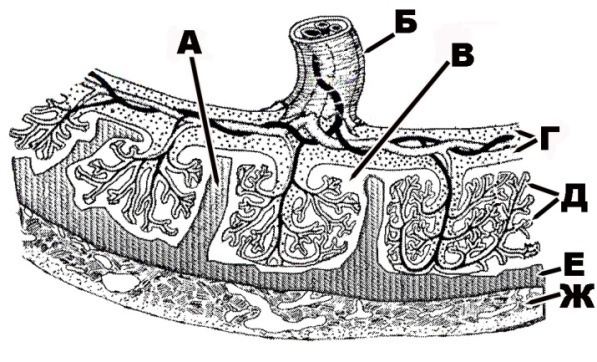
343. Human germinal structure that is designated with the letter A:
a. nerve tube
b. notochord
c. somites
d. +ectoderm
e. endoderm
344. Human germinal structure that is designated with the letter Б:
a. nerve tube
b. notochord
c. +somites
d. ectoderm
e. endoderm
345. Human germinal structure that is designated with the letter B:
a. +nerve tube
b. notochord
c. somites
d. ectoderm
e. endoderm
346. Human germinal structure that is designated with the letter Г:
a. nerve tube
b. notochord
c. somites
d. +parietal layer of the mesoderm
e. endoderm
347. Human germinal structure that is designated with the letter Д:
a. nerve tube
b. notochord
c. somites
d. ectoderm
e. +visceral layer of the mesoderm
348. Human germinal structure that is designated with the letter E:
a. nerve tube
b. notochord
c. somites
d. ectoderm
e. +endoderm
349. Human germinal structure that is designated with the letter Ж:
a. nerve tube
b. +notochord
c. somites
d. ectoderm
e. endoderm
|
350. Human placental structure that is designated with the letter A:
a. +septa
b. umbilical cord
c. lacunae
d. chorionic plate
e. chorionic villi
351. Human placental structure that is designated with the letter Б:
a. septa
b. +umbilical cord
c. lacunae
d. chorionic plate
e. chorionic villi
352. Human placental structure that is designated with the letter B:
a. septa
b. umbilical cord
c. +lacunae
d. chorionic plate
e. chorionic villi
353. Human placental structure that is designated with the letter Г:
a. septa
b. umbilical cord
c. lacunae
d. +chorionic plate
e. chorionic villi
354. Human placental structure that is designated with the letter Д:
a. septa
b. umbilical cord
c. lacunae
d. chorionic plate
e. +chorionic villi
355. Human placental structure that is designated with the letter E:
a. septa
b. umbilical cord
c. lacunae
d. +endometrium
e. chorionic villi
356. Human placental structure that is designated with the letter Ж:
a. septa
b. umbilical cord
c. lacunae
d. endometrium
e. +myometrium
|
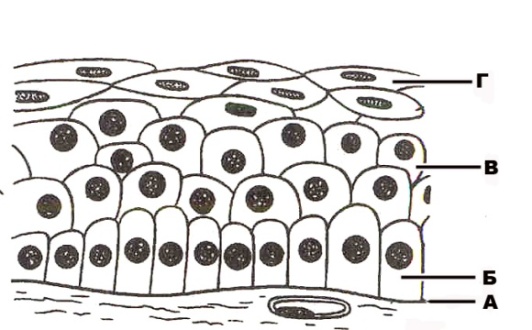
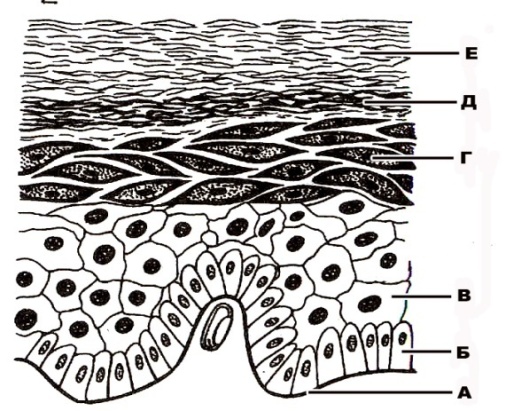
357. Structure of stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium that is designated with the letter A:
a. vessel
b. +basement membrane
c. basal layer
d. layer of polyhedral cells
e. layer of flattened cells
358. Structure of stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium that is designated with the letter Б:
a. vessel
b. basement membrane
c. +basal layer
d. layer of polyhedral cells
e. layer of flattened cells
359. Structure of stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium that is designated with the letter B:
a. vessel
b. basement membrane
c. basal layer
d. +layer of polyhedral cells
e. layer of flattened cells
360. Structure of stratified squamous non-keratinized epithelium that is designated with the letter Г:
a. vessel
b. basement membrane
c. basal layer
d. layer of polyhedral cells
e. +layer of flattened cells
|
361. Structure of stratified squamous keratinized epithelium that is designated with the letter A:
a. +basement membrane
b. basal layer
c. stratum spinosum (Malpighian layer)
d. stratum granulosum
e. stratum lucidum
362. Structure of stratified squamous keratinized epithelium that is designated with the letter Б:
a. basement membrane
b. +basal layer
c. stratum spinosum (Malpighian layer)
d. stratum granulosum
e. stratum lucidum
363. Structure of stratified squamous keratinized epithelium that is designated with the letter B:
a. basement membrane
b. basal layer
c. +stratum spinosum (Malpighian layer)
d. stratum granulosum
e. stratum lucidum
364. Structure of stratified squamous keratinized epithelium that is designated with the letter Г:
a. basement membrane
b. basal layer
c. stratum spinosum (Malpighian layer)
d. +stratum granulosum
e. stratum lucidum
365. Structure of stratified squamous keratinized epithelium that is designated with the letter Д:
a. basement membrane
b. basal layer
c. stratum spinosum (Malpighial layer)
d. stratum granulosum
e. +stratum lucidum
366. Structure of stratified squamous keratinized epithelium that is designated with the letter E:
a. +stratum corneum
b. stratum basale
c. stratum spinosum (Malpighian layer)
d. stratum granulosum
e. stratum lucidum
|
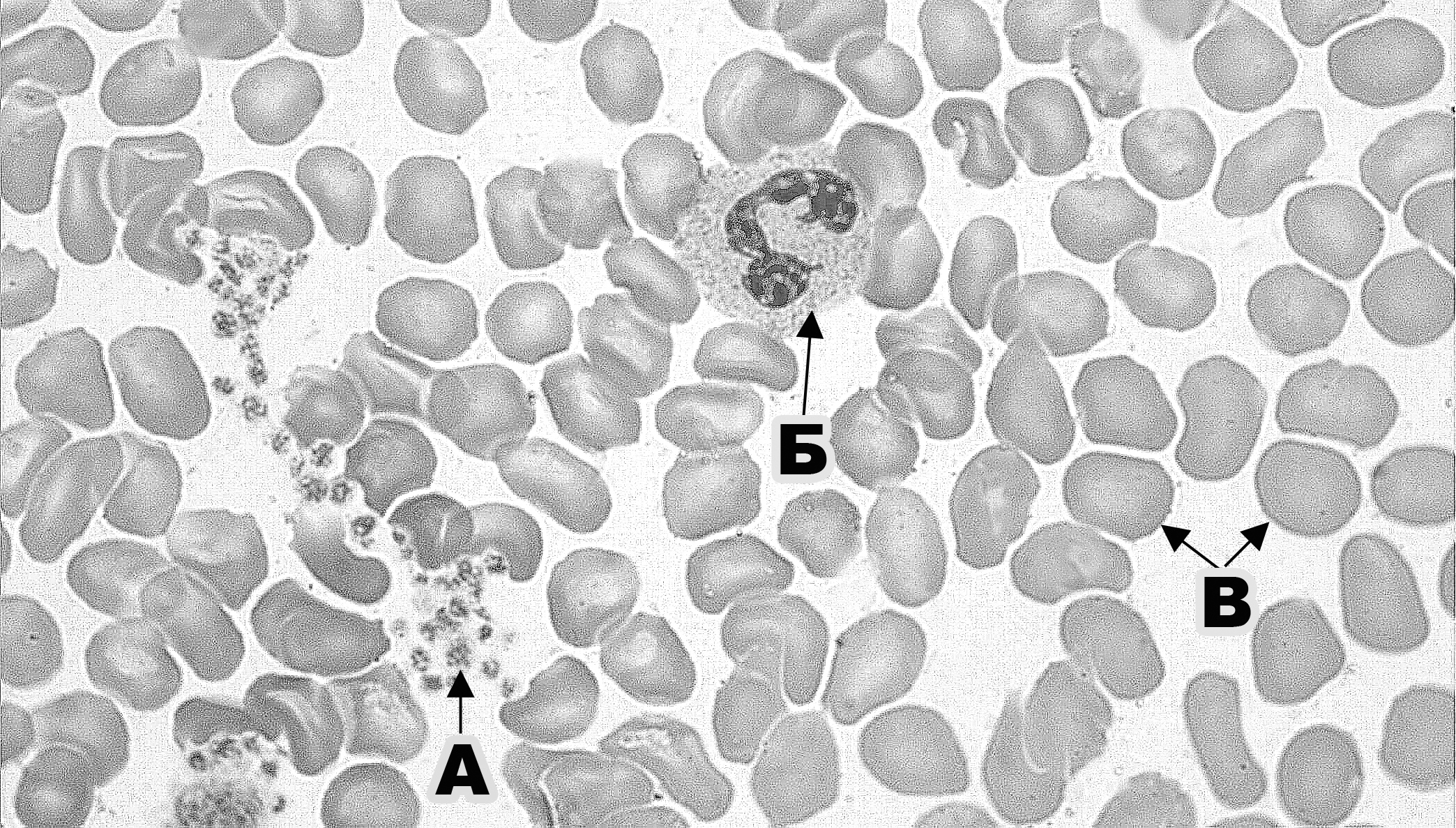
367. Formed element of blood (at the magnification of 630) that is designated with the letter A:
a. erythrocyte
b. +thrombocyte
c. neutrophil
d. basophil
e. small lymphocyte
368. Formed element of blood (at the magnification of 630) that is designated with the letter Б:
a. erythrocyte
b. thrombocyte
c. +neutrophil
d. basophil
e. small lymphocyte
369. Formed element of blood (at the magnification of 630) that is designated with the letter B:
a. +erythrocyte
b. thrombocyte
c. neutrophil
d. basophil
e. small lymphocyte
|
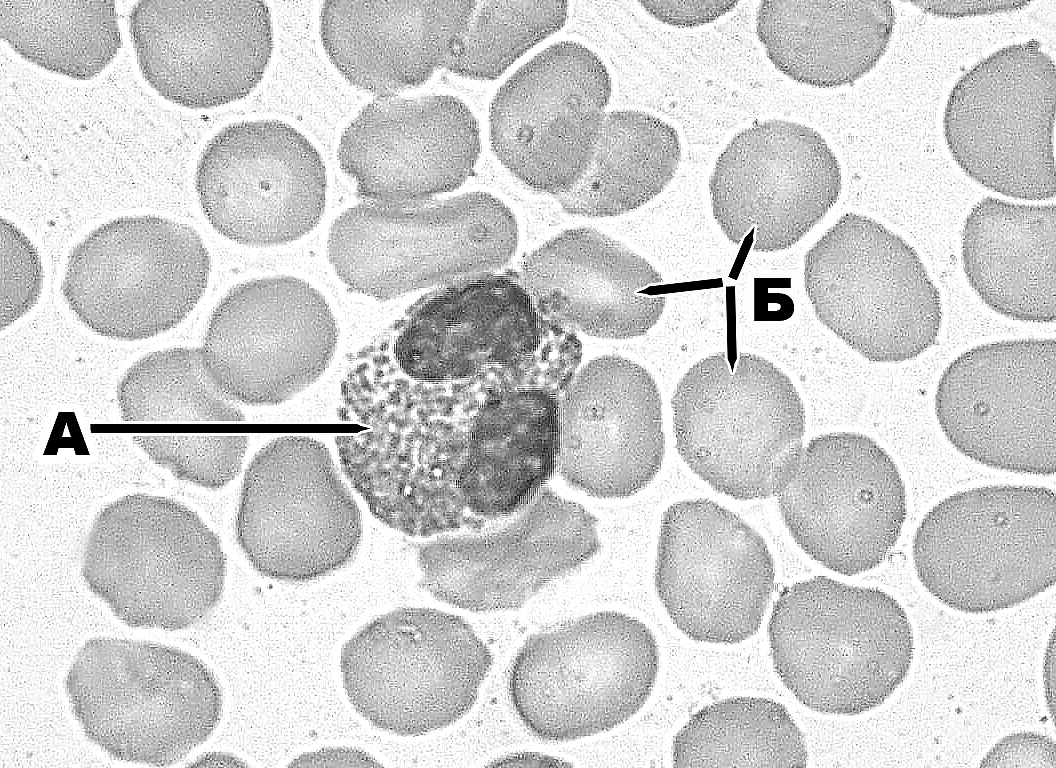
370. Formed element of blood (at the magnification of 1000) that is designated with the letter A:
a. erythrocyte
b. thrombocyte
c. neutrophil
d. basophil
e. +small lymphocyte
371. Formed element of blood (at the magnification of 1000) that is designated with the letter Б:
a. +erythrocyte
b. thrombocyte
c. neutrophil
d. basophil
e. small lymphocyte
|
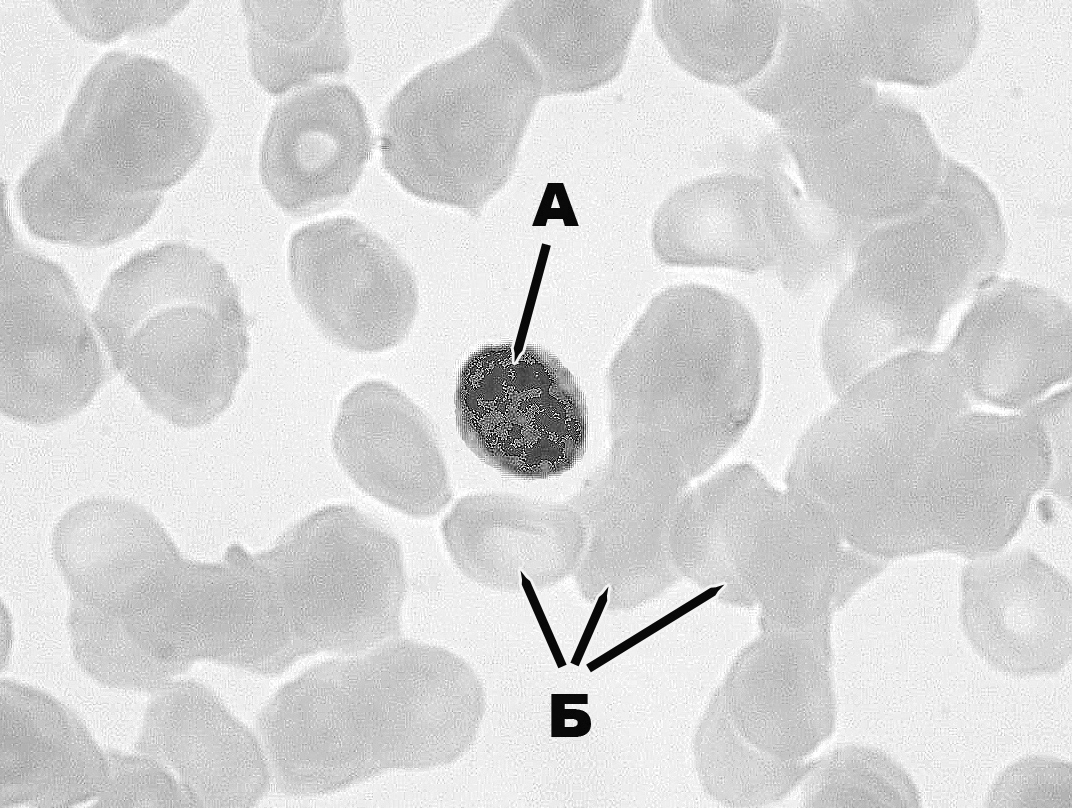
372. Formed element of blood (at the magnification of 1000) that is designated with the letter A:
a. erythrocyte
b. eosinophil
c. neutrophil
d. basophil
e. +large lymphocyte
373. Formed element of blood (at the magnification of 1000) that is designated with the letter Б:
a. +erythrocyte
b. eosinophil
c. neutrophil
d. basophil
e. large lymphocyte
|
374. Formed element of blood (at the magnification of 1000) that is designated with the letter A:
a. erythrocyte
b. eosinophil
c. neutrophil
d. basophil
e. +mall lymphocyte
375. Formed element of blood (at the magnification of 1000) that is designated with the letter Б:
a. +erythrocyte
b. eosinophil
c. neutrophil
d. basophil
e. small lymphocyte
|
376. Structure of the loose irregular fibrous connective tissue that is designated with the letter A:
a. +mast cell
b. collagen fibre
c. macrophages
d. elastic fibre
e. ground substance
377. Structure of the loose irregular fibrous connective tissue that is designated with the letter Б:
a. mast cell
b. +collagen fibre
c. macrophages
d. elastic fibre
e. ground substance
378. Structure of the loose irregular fibrous connective tissue that is designated with the letter B:
a. mast call
b. collagen fibre
c. +macrophages
d. elastic fibre
e. ground substance
379. Structure of the loose irregular fibrous connective tissue that is designated with the letter Г:
a. mast cell
b. collagen fibre
c. macrophages
d. +elastic fibre
e. ground substance
380. Structure of the loose irregular fibrous connective tissue that is designated with the letter Д:
a. mast cell
b. collagen fibre
c. macrophages
d. elastic fibre
e. +ground substance
381. Structure of the loose irregular connective tissue that is designated with the letter E:
a. mast cell
b. collagen fibre
c. macrophages
d. elastic fibre
e. +fibroblast
382. Structure of the loose irregular fibrous connective tissue that is designated with the letter Ж:
a. mast cell
b. collagen fibre
c. +adipose cell
d. elastic fibre
e. ground substance
|
383. Structure of hyaline cartilage that is designated with the letter A:
a. +perichondrium
b. zone of young cartilage
c. zone of mature cartilage
d. young chondrocytes
e. isogenous cell groups (cell-nests)
384. Structure of hyaline cartilage that is designated with the letter Б:
a. perichondrium
b. +zone of young cartilage
c. zone of mature cartilage
d. young chondrocytes
e. isogenous cell groups (cell-nests)
385. Structure of hyaline cartilage that is designated with the letter B:
a. perichondrium
b. zone of young cartilage
c. +zone of mature cartilage
d. young chondrocytes
e. isogenous cell groups (cell-nests)
386. Structure of hyaline cartilage that is designated with the letter Г:
a. perichondrium
b. zone of young cartilage
c. zone of mature cartilage
d. +young chondrocytes
e. isogenous cell groups (cell-nests)
387. Structure of hyaline cartilage that is designated with the letter Д:
a. perichondrium
b. zone of young cartilage
c. zone of mature cartilage
d. young chondrocytes
e. +isogenous cell groups (cell-nests)
|
388. Structure of lamellar bone that is designated with the letter A:
a. layer of the inner circumferential lamellae
b. Haversian canal
c. interstitial lamellae
d. osteon
e. +layer of the outer circumferential lamellae
389. Structure of lamellar bone that is designated with the letter Б:
a. layer of the inner circumferential lamellae
b. Haversian canal
c. interstitial lamellae
d. +osteon
e. layer of the outer circumferential lamellae
390. Structure of lamellar bone that is designated with the letter B:
a. layer of the inner circumferential lamellae
b. Haversian canal
c. +interstitial lamellae
d. osteon
e. layer of the outer circumferential lamellae
391. Structure of lamellar bone that is designated with the letter Г:
a. layer of the inner circumferential lamellae
b. +Haversian canal
c. interstitial lamellae
d. osteon
e. layer of the outer circumferential lamellae
392. Structure of lamellar bone that is designated with the letter Д:
a. +layer of the inner circumferential lamellae
b. Haversian canal
c. interstitial lamellae
d. osteon
e. layer of the outer circumferential lamellae
|
393. Bone cell that is designated with the letter A:
a. dormant osteoblast
b. mature osteoblast
c. osteocyte of the first type
d. +“resorbing” osteocyte
e. osteoclast
394. Bone cell that is designated with the letter Б:
a. dormant osteoblast
b. +mature osteoblast
c. osteocyte of the first type
d. “resorbing” osteocyte
e. osteoclast
395. Bone cell that is designated with the letter B:
a. dormant osteoblast
b. mature osteoblast
c. osteocyte of the first type
d. “resorbing” osteocyte
e. +osteoclast
|
396. Structure of smooth muscle that is designated with the letter A:
a. loose irregular fibrous connective tissue
b. longitudinal section of the smooth muscle cell
c. +transverse section of the smooth muscle cell
d. vessel
e. fibroblast
397. Structure of smooth muscle that is designated with the letter Б:
a. +loose irregular fibrous connective tissue
b. longitudinal section of the smooth muscle cell
c. transverse section of the smooth muscle cell
d. vessel
e. fibroblast
398. Structure of smooth muscle that is designated with the letter B:
a. loose irregular fibrous connective tissue
b. +longitudinal section of the smooth muscle cell
c. transverse section of the smooth muscle cell
d. vessel
e. fibroblast
|
399. Structure of the striated muscle that is designated with the letter A:
a. longitudinal sections of the striated muscle fibres
b. transverse sections of the striated muscle fibres
c. +loose irregular fibrous connective tissue
d. nuclei of the muscle fibres
e. fibroblasts
400. Structure of the striated muscle that is designated with the letter Б:
a. +longitudinal sections of the striated muscle fibres
b. transverse sections of the striated muscle fibres
c. loose irregular fibrous connective tissue
d. nuclei of the muscle fibres
e. fibroblasts
401. Structure of the striated muscle that is designated with the letter B:
a. longitudinal sections of the striated muscle fibres
b. transverse sections of the striated muscle fibres
c. loose irregular fibrous connective tissue
d. +nuclei of the muscle fibres
e. fibroblasts
402. Structure of the striated muscle that is designated with the letter Г:
a. longitudinal sections of the striated muscle fibres
b. +transverse sections of the striated muscle fibres
c. loose irregular fibrous connective tissue
d. nuclei of the muscle fibres
e. fibroblasts
|
403. Structure of the sarcomere that is designated with the letter A:
a. H-zone
b. +Z-band
c. M-band
d. actin filaments
e. myosin filaments
404. Structure of the sarcomere that is designated with the letter Б:
a. H-zone
b. Z-band
c. M-band
d. +actin filaments
e. myosin filaments
405. Structure of the sarcomere that is designated with the letter B:
a. H-zone
b. Z-band
c. +M-band
d. actin filamements
e. myosin filaments
406. Structure of the sarcomere that is designated with the letter Г:
a. H-zone
b. Z-band
c. M-band
d. actin filaments
e. +myosin filaments
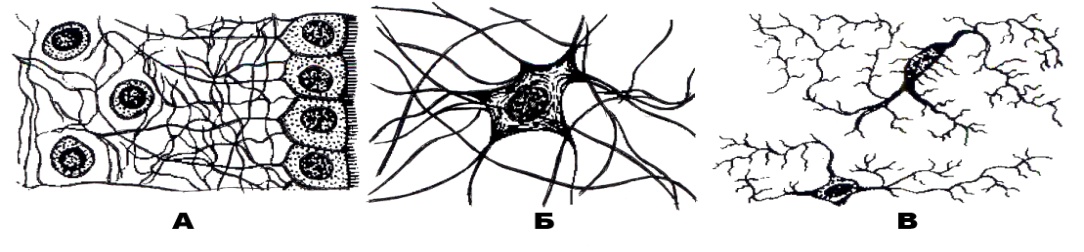
|
407. Type of necroglia that is designated with the letter A:
Читайте також:
- Advantages of Computer Data Processing.
- Advantages of Computer Data Processing.
- ALU Architecture for Processing
- AND DATA PROCESSING IN MODERN SOCIETY
- AT DINNER
- Consumer Decision-Making Process
- Ex. 12. Dinner-table Talk
- Food processing. Translate the text into your own language
- Microprocessor System
- Neuromuscular synapse includes a process of a nerve cell. What process is it? What type of neurocyte does that process belong to?
- Objectively and subjectively conditioned transformations of lexical units in the process of translation.
| <== попередня сторінка | | | наступна сторінка ==> |
| Neuromuscular synapse includes a process of a nerve cell. What process is it? What type of neurocyte does that process belong to? | | | a. protoplasmatic astrocyte |
|
Не знайшли потрібну інформацію? Скористайтесь пошуком google: |
© studopedia.com.ua При використанні або копіюванні матеріалів пряме посилання на сайт обов'язкове. |