
- Гідрологія і Гідрометрія
- Господарське право
- Економіка будівництва
- Економіка природокористування
- Економічна теорія
- Земельне право
- Історія України
- Кримінально виконавче право
- Медична радіологія
- Методи аналізу
- Міжнародне приватне право
- Міжнародний маркетинг
- Основи екології
- Предмет Політологія
- Соціальне страхування
- Технічні засоби організації дорожнього руху
- Товарознавство продовольчих товарів
Тлумачний словник
Авто
Автоматизація
Архітектура
Астрономія
Аудит
Біологія
Будівництво
Бухгалтерія
Винахідництво
Виробництво
Військова справа
Генетика
Географія
Геологія
Господарство
Держава
Дім
Екологія
Економетрика
Економіка
Електроніка
Журналістика та ЗМІ
Зв'язок
Іноземні мови
Інформатика
Історія
Комп'ютери
Креслення
Кулінарія
Культура
Лексикологія
Література
Логіка
Маркетинг
Математика
Машинобудування
Медицина
Менеджмент
Метали і Зварювання
Механіка
Мистецтво
Музика
Населення
Освіта
Охорона безпеки життя
Охорона Праці
Педагогіка
Політика
Право
Програмування
Промисловість
Психологія
Радіо
Регилия
Соціологія
Спорт
Стандартизація
Технології
Торгівля
Туризм
Фізика
Фізіологія
Філософія
Фінанси
Хімія
Юриспунденкция
Formats of instructions
FEATURES OF COMPUTERS INSTRUCTIONS SETS OF OF IFFERENT ARCHITECTURE. CLASSIFICATION OF COMMANDS. FORMATS OF COMMANDS. METHODS OF DATA ADRESSING.
Контрольні питання
Висновки
Розглянуті "Правила організації захисту електронних банківських документів" в цілому регламентують:
порядок отримання, обліку, передачі, використання та зберігання засобів криптозахисту НБУ,
правила інформаційної безпеки
в установах, що є учасниками інформаційно-обчислювальної мережі Національного банку України.
"Правила зберігання, захисту, використання та розкриття банківської таємниці" регламентують організаційно-технічні заходи при здійсненні захисту банківської таємниці.
- Якими рубежами захисту системи сигналізації повинно бути обладнане приміщення АРМ-НБУ?
- Хто має право доступу в приміщення АРМ-НБУ?
- Чи допускаються співробітники банківської установи до приміщення АРМ-НБУ?
- Які вимоги висуваються до робочого місця адміністратора захисту інформації?
- Яка мета криптографічного захисту інформації в інформаційно-обчислювальній мережі НБУ?
- За допомогою яких засобів виконується криптографічний захист електронних банківських документів в установах, що є учасниками інформаційно-обчислювальної мережі НБУ?
- Із яких частин складаються засоби апаратного шифрування інформаційно-обчислювальної мережі НБУ?
- Хто здійснює генерацію ключів ЕЦП для операціоністів та бухгалтерів?
- Що необхідно зробити після генерації ключів?
- Хто у банківській установі займається діловодством з питань організації системи захисту інформації в інформаційно-обчислювальній мережі НБУ?
- При організації діловодства які документи повинен вести адміністратор захисту інформації?
- У яких випадках банківська установа зобов'язана негайно (по телефону) інформувати службу захисту інформації регіонального управління НБУ?
- Що входить в перелік найсерйозніших порушень в організації роботи із засобами захисту інформації Національного банку України?
- Яким є основний захід із забезпечення зберігання та захисту банківської таємниці?
- Дотримання яких вимог мають забезпечити банки під час роботи з документами, що містять банківську таємницю, на електронних носіях?
Any COMPUTER instruction is some well-organized sequence of bits, which determines:
1. Operation, initiated by this instruction.
2. Addresses of operands participating in this operation.
Therefore in majority of COMPUTER an instruction has the operation-address system.

In operation part from point of machine presentation an operation code is written.
And the code of operands addresses is set in address part. It contains information not only about the addresses of operands and result of operation but also about a next instruction address.
Under the format of commandcomposition, purpose and location of the separate instruction fields, is understood.
Development of structure takes a place only at diminishing of the address field (SISC processors). With appearance of RISC processors a return happened to extended addressness of instructions set. Speaking about a base level, speech goes about SISC processors. Originally the instructions set had the following format:

A3 :=(A1)*(A2) СIAdd:=A4
CIAdd – counter of instruction address.
* - operation
(х) – content of address х
A next instruction (it is the most universal variant) address is set in every command, but such instruction length is great. At such instructions set they can be located in any order, but usually try to locate consistently. Such order is called natural, but at a natural location a necessity falls off for the field A4.
Consequently, a format will have a kind:

A3 := (A1)*(A2)
CIAdd := (CIAdd)+1
Even passing to such format poorly diminishes instruction length. Most calculations have a recurrent chart of calculations, consequently, two address instructions set can be done .
(A1) := (A1)*(A2)
CIAdd := (CIAdd)+1
Such chart of calculations is basic for modern COMPUTERS.
But development went also in direction of processor development and its internal memory, it resulted in that the special registers which are always used in calculations appeared in processors. АСС := (АСС)*Y
If accumulatoe principle is used, for the instructions set it is enough to use one address. 
An instruction can be not adressed some times, if the instruction sets an operation over the fixed addresses (for example, action over accumulators), in the format of such instructions the address field absents. An instruction is called zeroaddress. A high-quality comparative analysis shows:
1. Short instructions are preferably than long, because occupy less memory. Any memory of COMPUTER is characterized by speed of transmission (by a carrying capacity). If a physical fast-acting is fixed, amount of selectable from memory instructions, inversely proportional to instruction length. And speed of processor work for short commands is greater than for long . Short instructions increase the productivity of processor. For most modern COMPUTERS a processor works quick than memory, consequently, to provide a high performance, it is needed to increase the amount of commands that are extracted from memory for one access cycle.
2. The formats of instructions must provide sufficient space for of all operations setting (if the computer system plugs in itself N of operations of nmin= ] log2n [ it is rounding in a greater side)
3. Instruction length must be multiple to the length of the base informative one (it means that instruction must occupy an integer number of bytes or words, or in one word must be an integer number of instructions). If in one word is not integer number of commands, in this case the memory is not fully used or procedures of cinstruction hoice are complicated. In addition, instruction length must be chosen taking into account length of the processed data characters codes.
4. Length of the instruction address field is very closely related to organization of computer memory, and also with the size of address space of memory which can be directly adressed in computer memory. If memory includes M address elements, then minimum length of the address field is: mmin=]log2M[. If to come from the fixed length of the address field, the capacity of memory will depend on minimum adressed information unit.
There are two methods of tasks decision at the limited instruction word:
1. By the variable instruction lengt usage.
2. By the instruction code expansion.
For the often used operations set , as a rule, the short code of operations is used, and in combination with the short address field we will get short instructions, it gives:
1. Good memory usage;
2. Maximally possible speed of treatment.
For other less often iused operations and actions set, more long code fields are used (it can be without the instruction length changing).
Let present two-bytes instruction :
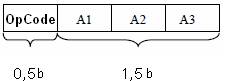 (A3)*(A2)⇒A1
(A3)*(A2)⇒A1
How it is possible to change the address field length without instruction length changing?
It is possible to forbid a record in a cell with an address 0000. A1 is an address of receiver.
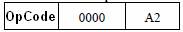
The format of address part is changed, and address space increased to 256 elements. But most commands related to SISC processors have variable instructions length:

0000 – designates that A1 and A2 are increased in two times.
If it is required more extend the address space, it is possible, by using the principle of variable instruction length, to define that 0000 means that length of the address field, for example, became 5 byte.
How is it possible to increase the set of operations?

Читайте також:
- Arithmetic Instructions
- Branch Instructions
- Computer Instructions
- Conditional Branch Instructions
- Data Transfer Instructions
- Instructions of data handling
- Symbolic Microinstructions
| <== попередня сторінка | | | наступна сторінка ==> |
| Особливості розкриття інформації, що містить банківську таємницю, Національному банку | | |
|
Не знайшли потрібну інформацію? Скористайтесь пошуком google: |
© studopedia.com.ua При використанні або копіюванні матеріалів пряме посилання на сайт обов'язкове. |