
- Гідрологія і Гідрометрія
- Господарське право
- Економіка будівництва
- Економіка природокористування
- Економічна теорія
- Земельне право
- Історія України
- Кримінально виконавче право
- Медична радіологія
- Методи аналізу
- Міжнародне приватне право
- Міжнародний маркетинг
- Основи екології
- Предмет Політологія
- Соціальне страхування
- Технічні засоби організації дорожнього руху
- Товарознавство продовольчих товарів
Тлумачний словник
Авто
Автоматизація
Архітектура
Астрономія
Аудит
Біологія
Будівництво
Бухгалтерія
Винахідництво
Виробництво
Військова справа
Генетика
Географія
Геологія
Господарство
Держава
Дім
Екологія
Економетрика
Економіка
Електроніка
Журналістика та ЗМІ
Зв'язок
Іноземні мови
Інформатика
Історія
Комп'ютери
Креслення
Кулінарія
Культура
Лексикологія
Література
Логіка
Маркетинг
Математика
Машинобудування
Медицина
Менеджмент
Метали і Зварювання
Механіка
Мистецтво
Музика
Населення
Освіта
Охорона безпеки життя
Охорона Праці
Педагогіка
Політика
Право
Програмування
Промисловість
Психологія
Радіо
Регилия
Соціологія
Спорт
Стандартизація
Технології
Торгівля
Туризм
Фізика
Фізіологія
Філософія
Фінанси
Хімія
Юриспунденкция
Military Ranks
(US Views)
One big problem throughout military history has been identifying who's in charge. From the earliest days of warfare to the present, special rank badges meant survival. In the heat of battle, knowing who to listen to was as important as the fighting skills soldiers and sailors developed. They had to know at a glance whose shouted orders toobey.
The U.S. military services still use many of the ranks they started with when they began in 1775 at the outbreak of the Revolutionary War. The leaders adopted the organization, regulations and ranks of the British army and navy with just minor changes. This is not surprising because the Revolutionary Army was made up of colonial militia units that had been organized and drilled by British methods for many years.
Revolutionary Army rank insignia, however, did not follow the British patterns but was similar to the insignia used by the French. After the war the U.S. Army often used the uniform styles and some insignia of the British as well as the French armies.
Military rank is more than just who salutes whom. Military rank is a badge of leadership. Responsibility forpersonnel, equipment, and mission grows with each increase in rank.
Officer ranks in the United States military consist of commissioned officers (ComOs)and warrant officers (WOs). The commissioned ranks are the highest in the military. These officers hold presidential commissions and are confirmed at their ranks by the Senate. Army, Air Force and Marine Corps officers are called company grade officers in the pay grades of O-1 to O-3, field grade officers in pay grades O-4 to O-6 and general officers in pay grades O-7 and higher. The equivalent officer groupings in the Navy are called junior grade, mid-grade and flag.
Warrant officers hold warrants from their service secretary and are specialists and experts in certain military technologies or capabilities. The lowest ranking warrant officers serve under a warrant, but they receive commissions from the president upon promotion to chief warrant officer 2. These commissioned warrant officers are direct representatives of the president of the United States. They derive their authority from the same source as commissioned officers but remain specialists, in contrast to commissioned officers, who are generalists. There are no warrant officers in the Air Force.
Non-commissioned officers (NCOs) are servicepeople who have received neither a commission nor a warrant but hold positions requiring responsibility for personnel and its training. They may be sergeants or petty officers in the Navy.
The lowest in the rank are the enlisted personnel. However, depending on their qualification and service aptitudes they are also differentiated in rank.
Do not confuse rank with pay grades, such as E-1, W-2 and O-5. Pay grades are administrative classifications used primarily to standardizecompensation across the military services. The "E" in E-1 stands for "enlisted" while the “1” indicates the pay grade for that position. The other pay categories are “W” for warrant officers and "O" for commissioned officers. Some enlisted pay grades have two ranks.
The Army, for example, has the ranks of corporal and specialist at the pay grade of E-4. A corporal is expected to fill a leadership role and has a higher rank than a specialist even though both receive the same amount of pay.
Pay grade is used in the US military as to normalize the equivalent enlisted and officer ranks respectively. For example, the base pay of an E-8 are the same in the Air Force and the Army. In theory, those two E-8s will have equivalent levels of seniority and responsibility.
The table shows current ranks in the US military service branches, but they can serve as a fair guide throughout the twentieth century. [53]
| W1 | Warrant Officer 1 WO1 
| Warrant Officer 1 W-1 *The grade of Warrant Officer W-1 is no longer in use. | Warrant
Officer 1 WO 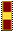
| NO WARRANT |
| W2 | Chief Warrant Officer 2 CW2 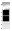
| Chief Warrant Officer 2 CWO2 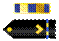
| Chief Warrant Officer 2 CWO2 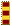
| NO WARRANT |
| W3 | Chief Warrant Officer 3 CW3 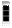
| Chief Warrant Officer 3 CWO3 
| Chief Warrant Officer 3 CWO3 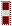
| NO WARRANT |
| W4 | Chief Warrant Officer 4, CW4 
| Chief Warrant Officer 4, CWO4 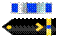
| Chief Warrant Officer 4, CWO4 
| NO WARRANT |
| W5 | Chief Warrant Officer CW5 
| NO CHIEF WARRANT OFFICER CWO5 | Chief Warrant Officer 5, CWO5 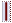
| NO WARRANT |

| 
| 
| 
| |
| ||||
| O1 | Second Lieutenant 2LT 
| Ensign, ENS
| Second Lieutenant 2nd Lt. 
| Second Lieutenant 2nd Lt. 
|
| O2 | First Lieutenant 1LT 
| Lieutenant Junior Grade, LTJG 
| First Lieutenant 1st Lt. 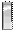
| First Lieutenant 1st Lt. 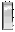
|
| O3 | Captain CPT 
| Lieutenant, LT 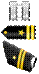
| Captain Capt. 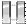
| Captain Capt. 
|
| O4 | Major MAJ 
| Lieutenant Commander, LCDR 
| Major Maj. 
| Major Maj. 
|
| O5 | Lieutenant Colonel LTC 
| Commander CDR
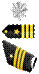
| Lieutenant Colonel Lt. Col. 
| Lieutenant Colonel Lt. Col. 
|
| O6 | Colonel COL 
| Captain CAPT 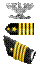
| Colonel COL

| Colonel COL.

|
| O7 | Brigadier General BG 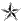
| Rear Admiral Lower Half RADM (LH) 
| Brigadier General BG 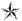
| Brigadier General BG 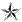
|
| O8 | Major General MG 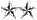
| Rear Admiral Upper Half RADM (UH) 
| Major General Maj. Gen. 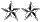
| Major General Maj. Gen. 
|
| O9 | Lieutenant General LTG 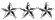
| Vice Admiral VADM 
| Lieutenant General Lt. Gen. 
| Lieutenant General Lt. Gen. 
|
| O10 | General GEN Army Chief of Staff 
| Admiral ADM Chief of Naval Operations and Commandant of the Coast Guard 
| General Gen. Commandant of the Marine Corps 
| General Gen. Air Force Chief of Staff 
|
General of the Army (Reserved for wartime only) 
| Fleet Admiral (Reserved for wartime only) 
| General of the Air Force (Reserved for wartime only) 
|
| s | Answer the questions |
1. What groupings of officers do you know?
2. What is the difference between commissioned and non-commissioned officers?
3. What is a warrant?
4. What is the pay scale used for?
5. Are there any ranks for enlisted personnel?
| > | Read, decipher and translate abbreviations |
GA; BG; VADM; MSGT; GAF; GEN; SCPO; LTG; MG; COL; LTJG; LTC; MAJ; CPT; RADM; 1LT; 2LT; PO1; MWO; RCT; SMAJ; 1SGT; CPT; SFC; MCPO; SSGT; SGT; CPL; PFC; PVT; FADM; ADM; COMMO; CDR; LCDR; LT; ENS; CPO; NCO.
| N | O | 
| Translate into Ukrainian |
Badge of leadership; derive one’s authority; administrative classification; compensation; base pay; service aptitudes; fill a leadership role; hold a warrant; develop fighting skills; identify who's in charge; in the heat of battle; special rank badge; know at a glance; be differentiated in rank; at the outbreak of the Revolutionary War; depending on one’s qualification; follow the British patterns; military experience; confuse rank with pay grades; equivalent officer groupings; hold positions; responsibility for personnel and its training; minor change; shouted order; receive the same amount of pay.
| N | O | 
| Translate into English |
Розрізнятися у військовому званні; відповідальність за особовий склад та його бойову підготовку; службові здібності; в залежності від кваліфікації; службова класифікація; усний наказ; отримувати повноваження; виконувати командні функції; отримувати однакове грошове утримання; грошове забезпечення/утримання; впізнавати командира; незначні зміни; перебувати на посаді; військовий досвід; на початку війни за незалежність; спеціальна ознака військового звання; плутати військове звання зі штатно-посадовою категорією; мінімальне грошове утримання; миттєво впізнавати; використовувати британські зразки; в розпалі битви; розвивати бойові навички; ознака командира; відповідні категорії офіцерського складу; отримувати наказ міністра (СВ, ВПС, ВМС) про присвоєння військового звання ворент-офіцера.
| ó | N | O | 
| Translate quickly |
Виконувати накази; rank insignia; військове вітання; віддавати військове вітання; increase in rank; офіцерське звання; commissioned officer (ComO); ворент-офіцер; hold presidential commission; штатно-посадова категорія (за грошовим утриманням); тарифний розряд; company grade officers; старші офіцери; general officers; молодші офіцери (ВМС); mid-grade officers; адмірали; non-commissioned officers (NCOs); сержант; petty officer (РО); наказ про присвоєння військового звання ворент-офіцера; receive commission; підвищення у військовому званні; specialist; фахівець широкого профілю; enlisted personnel; посада; seniority; одержувати підтвердження Сенатом військового звання; be a direct representative of the president of the United States; військове звання; obey orders; знаки розрізнення за військовим званням; salute; підвищення у військовому званні; officer rank; офіцер; warrant officer (WO); отримати офіцерське звання від президента; pay grade; молодші офіцери; field grade officers; генерали; junior grade officers; старші офіцери (ВМС); flag officers; сержантський і старшинський склад; sergeant (SGT); старшина (ВМС); warrant; отримати офіцерське звання; promotion; спеціаліст (фахівець вузького профілю); generalist; рядовий склад; position; старшинство; be confirmed at one’s rank by the Senate; прямо призначатися президентом США.
| A | Build up your vocabulary |
rank
Читайте також:
- Basic Military Training
- Lesson 12 Military Ranks
- Lesson 13 Military Uniform
- Lesson 13 Military Uniform
- Lesson 17 Basic Military Training
- Lesson 22Military Topography
- Lesson 22Military Topography
- Seti wearing a blue crown to emphasize his military prowess, burns incense over an offering
- Seti wearing a blue crown to emphasize his military prowess, burns incense over an offering
- Typical Day at a Military Academy
| <== попередня сторінка | | | наступна сторінка ==> |
| Lesson 12 Military Ranks | | | Lesson 13 Military Uniform |
|
Не знайшли потрібну інформацію? Скористайтесь пошуком google: |
© studopedia.com.ua При використанні або копіюванні матеріалів пряме посилання на сайт обов'язкове. |