
МАРК РЕГНЕРУС ДОСЛІДЖЕННЯ: Наскільки відрізняються діти, які виросли в одностатевих союзах
РЕЗОЛЮЦІЯ: Громадського обговорення навчальної програми статевого виховання
ЧОМУ ФОНД ОЛЕНИ ПІНЧУК І МОЗ УКРАЇНИ ПРОПАГУЮТЬ "СЕКСУАЛЬНІ УРОКИ"
ЕКЗИСТЕНЦІЙНО-ПСИХОЛОГІЧНІ ОСНОВИ ПОРУШЕННЯ СТАТЕВОЇ ІДЕНТИЧНОСТІ ПІДЛІТКІВ
Батьківський, громадянський рух в Україні закликає МОН зупинити тотальну сексуалізацію дітей і підлітків
Відкрите звернення Міністру освіти й науки України - Гриневич Лілії Михайлівні
Представництво українського жіноцтва в ООН: низький рівень культури спілкування в соціальних мережах
Гендерна антидискримінаційна експертиза може зробити нас моральними рабами
ЛІВИЙ МАРКСИЗМ У НОВИХ ПІДРУЧНИКАХ ДЛЯ ШКОЛЯРІВ
ВІДКРИТА ЗАЯВА на підтримку позиції Ганни Турчинової та права кожної людини на свободу думки, світогляду та вираження поглядів
РЕЗОЛЮЦІЯ: Громадського обговорення навчальної програми статевого виховання
ЧОМУ ФОНД ОЛЕНИ ПІНЧУК І МОЗ УКРАЇНИ ПРОПАГУЮТЬ "СЕКСУАЛЬНІ УРОКИ"
ЕКЗИСТЕНЦІЙНО-ПСИХОЛОГІЧНІ ОСНОВИ ПОРУШЕННЯ СТАТЕВОЇ ІДЕНТИЧНОСТІ ПІДЛІТКІВ
Батьківський, громадянський рух в Україні закликає МОН зупинити тотальну сексуалізацію дітей і підлітків
Відкрите звернення Міністру освіти й науки України - Гриневич Лілії Михайлівні
Представництво українського жіноцтва в ООН: низький рівень культури спілкування в соціальних мережах
Гендерна антидискримінаційна експертиза може зробити нас моральними рабами
ЛІВИЙ МАРКСИЗМ У НОВИХ ПІДРУЧНИКАХ ДЛЯ ШКОЛЯРІВ
ВІДКРИТА ЗАЯВА на підтримку позиції Ганни Турчинової та права кожної людини на свободу думки, світогляду та вираження поглядів
Контакти
- Гідрологія і Гідрометрія
- Господарське право
- Економіка будівництва
- Економіка природокористування
- Економічна теорія
- Земельне право
- Історія України
- Кримінально виконавче право
- Медична радіологія
- Методи аналізу
- Міжнародне приватне право
- Міжнародний маркетинг
- Основи екології
- Предмет Політологія
- Соціальне страхування
- Технічні засоби організації дорожнього руху
- Товарознавство продовольчих товарів
Тлумачний словник
Авто
Автоматизація
Архітектура
Астрономія
Аудит
Біологія
Будівництво
Бухгалтерія
Винахідництво
Виробництво
Військова справа
Генетика
Географія
Геологія
Господарство
Держава
Дім
Екологія
Економетрика
Економіка
Електроніка
Журналістика та ЗМІ
Зв'язок
Іноземні мови
Інформатика
Історія
Комп'ютери
Креслення
Кулінарія
Культура
Лексикологія
Література
Логіка
Маркетинг
Математика
Машинобудування
Медицина
Менеджмент
Метали і Зварювання
Механіка
Мистецтво
Музика
Населення
Освіта
Охорона безпеки життя
Охорона Праці
Педагогіка
Політика
Право
Програмування
Промисловість
Психологія
Радіо
Регилия
Соціологія
Спорт
Стандартизація
Технології
Торгівля
Туризм
Фізика
Фізіологія
Філософія
Фінанси
Хімія
Юриспунденкция
Figure 42 A simple microscope. It produces
Virtual, magnified, and upright images
Opera or Field Glasses. - The opera glass consists of an objective LM which converges the rays toward the point S (Figure 43), but before they reach this point they pass through the diverging lens NP which replaces the eyepiece of the telescope. In passing through this diverging lens, the rays that were converging on entering it are made to diverge on leaving it. To an eye on the right-hand side of the lens NP the rays seem to have come from a point A' behind the concave lens NP, which thus forms the virtual and erect image A'B' of the object from which light was received. Unlike the astronomical telescope, the opera glass gives an erect image. To have the opera glass in focus, the lens NP must be so placed with respect to the objective that the rays emerging from the lens NP are nearly parallel.
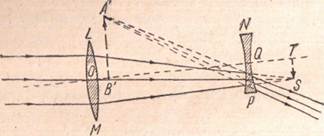
Figure 43 - Opera or field glasses. They produce
| <== попередня сторінка | | | наступна сторінка ==> |
| And magnified images | | | Virtual and upright images |
|
Не знайшли потрібну інформацію? Скористайтесь пошуком google: |
© studopedia.com.ua При використанні або копіюванні матеріалів пряме посилання на сайт обов'язкове. |