
- Гідрологія і Гідрометрія
- Господарське право
- Економіка будівництва
- Економіка природокористування
- Економічна теорія
- Земельне право
- Історія України
- Кримінально виконавче право
- Медична радіологія
- Методи аналізу
- Міжнародне приватне право
- Міжнародний маркетинг
- Основи екології
- Предмет Політологія
- Соціальне страхування
- Технічні засоби організації дорожнього руху
- Товарознавство продовольчих товарів
Тлумачний словник
Авто
Автоматизація
Архітектура
Астрономія
Аудит
Біологія
Будівництво
Бухгалтерія
Винахідництво
Виробництво
Військова справа
Генетика
Географія
Геологія
Господарство
Держава
Дім
Екологія
Економетрика
Економіка
Електроніка
Журналістика та ЗМІ
Зв'язок
Іноземні мови
Інформатика
Історія
Комп'ютери
Креслення
Кулінарія
Культура
Лексикологія
Література
Логіка
Маркетинг
Математика
Машинобудування
Медицина
Менеджмент
Метали і Зварювання
Механіка
Мистецтво
Музика
Населення
Освіта
Охорона безпеки життя
Охорона Праці
Педагогіка
Політика
Право
Програмування
Промисловість
Психологія
Радіо
Регилия
Соціологія
Спорт
Стандартизація
Технології
Торгівля
Туризм
Фізика
Фізіологія
Філософія
Фінанси
Хімія
Юриспунденкция
Machine epsilon
We know that a computer has a finite word length, so only a fixed number of digits is stored and used during computation. Hence, even in storing an exact decimal number in its converted form in the computer memory, an error is introduced. This error is machine dependant and is called machine epsilon.
Error= True value– Approximate value
In any numerical computation, we come across the following types of errors:
(1) Inherent errors.Errors which are already present in the statement of a problem before its solution are called inherent errors. Such errors arise either due to the fact that the given data is approximate or due to limitations of mathematical tables, calculators, or the digital computer.
Inherent errors can be minimized by taking better data or by using high precision* computing aids. Accuracy refers to the number of significant
digits in a value, for example, 53.965 is accurate to 5 significant digits.
Precision refers to the number of decimal positions or order of magnitude of the last digit in the value. For example, in 53.965, precision is 10–3.
Example.Which of the following numbers has the greatest precision?
4.3201, 4.32, 4.320106.
Sol.In 4.3201, precision is 10–4
In 4.32, precision is 10–2
In 4.320106, precision is 10–6.
Hence, the number 4.320106 has the greatest precision.
(2) Rounding errors.Rounding errors arise from the process of roundingoff numbers during the computation. They are also called procedural errors or numerical errors. Such errors are unavoidable in most of the calculations due to limitations of computing aids.
These errors can be reduced, however, by
(i) changing the calculation procedure so as to avoid subtraction of nearly equal numbers or division by a small number
(ii) retaining at least one more significant digit at each step and rounding-off at the last step. Rounding-off may be executed in two ways:
(a) Chopping.In chopping, extra digits are dropped by truncation of number. Suppose we are using a computer with a fixed word length of four digits, then a number like 12.92364 will be stored as 12.92.
We can express the number 12.92364 in the floating print form as
True x = 12.92364 = 0.1292364 × 102 = (0.1292 + 0.0000364) × 102 =
= 0.1292 × 102 + 0.364 × 10–4 + 2 = fx 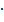 10E +gx10E – d = Approximate x + Error
10E +gx10E – d = Approximate x + Error
Error = gx 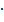 10E – d, 0 ≤ gx ≤ d
10E – d, 0 ≤ gx ≤ d
Here, gx is the mantissa, d is the length of mantissa and E is exponent
Since 0 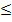 gx < 1
gx < 1
Absolute error 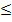 10E – d
10E – d
Case I.If gx < 0.5 then approximate x = fx 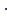 10E
10E
Case II.If gx ≥ .5 then approximate x = fx 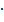 10E + 10E – d
10E + 10E – d
Error = True value – Approximate value
= fx 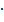 10E + gx . 10E – d– fx
10E + gx . 10E – d– fx 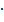 10E – 10E – d
10E – 10E – d
= (gx – 1) 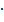 10E – d
10E – d
absolute error 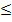 0.5
0.5 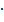 (10)E – d.
(10)E – d.
(b) Symmetric round-off.In symmetric round-off, the last retained significant digit is rounded up by unity if the first discarded digit is ≥ 5, otherwise the last retained digit is unchanged.
(3) Absolute error.Absolute error is the numerical difference between the true value of a quantity and its approximate value.
Thus, if X is the true value of a quantity and X` is its approximate value, then | X – X` | is called the absolute error ea.
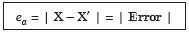
(4) Relative error.
The relative error er is defined by

where X is true value and X – X′ is error.
(6) Percentage error.Percentage error ep is defined as
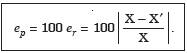
NOTE
1.The relative and percentage errors are independent of units used while absolute error is expressed in terms of these units.
2.If a number is correct to n decimal places, then the error = 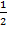
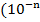 ).
).
e.g., if the number 3.1416 is correct to 4 decimal places, then the error = 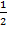
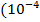 ) = .00005.
) = .00005.
3.If the first significant digit of a number is k and the number is correct to n significant digits, then the relative
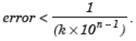
Переглядів: 181