
РЕЗОЛЮЦІЯ: Громадського обговорення навчальної програми статевого виховання
ЧОМУ ФОНД ОЛЕНИ ПІНЧУК І МОЗ УКРАЇНИ ПРОПАГУЮТЬ "СЕКСУАЛЬНІ УРОКИ"
ЕКЗИСТЕНЦІЙНО-ПСИХОЛОГІЧНІ ОСНОВИ ПОРУШЕННЯ СТАТЕВОЇ ІДЕНТИЧНОСТІ ПІДЛІТКІВ
Батьківський, громадянський рух в Україні закликає МОН зупинити тотальну сексуалізацію дітей і підлітків
Відкрите звернення Міністру освіти й науки України - Гриневич Лілії Михайлівні
Представництво українського жіноцтва в ООН: низький рівень культури спілкування в соціальних мережах
Гендерна антидискримінаційна експертиза може зробити нас моральними рабами
ЛІВИЙ МАРКСИЗМ У НОВИХ ПІДРУЧНИКАХ ДЛЯ ШКОЛЯРІВ
ВІДКРИТА ЗАЯВА на підтримку позиції Ганни Турчинової та права кожної людини на свободу думки, світогляду та вираження поглядів
- Гідрологія і Гідрометрія
- Господарське право
- Економіка будівництва
- Економіка природокористування
- Економічна теорія
- Земельне право
- Історія України
- Кримінально виконавче право
- Медична радіологія
- Методи аналізу
- Міжнародне приватне право
- Міжнародний маркетинг
- Основи екології
- Предмет Політологія
- Соціальне страхування
- Технічні засоби організації дорожнього руху
- Товарознавство продовольчих товарів
Тлумачний словник
Авто
Автоматизація
Архітектура
Астрономія
Аудит
Біологія
Будівництво
Бухгалтерія
Винахідництво
Виробництво
Військова справа
Генетика
Географія
Геологія
Господарство
Держава
Дім
Екологія
Економетрика
Економіка
Електроніка
Журналістика та ЗМІ
Зв'язок
Іноземні мови
Інформатика
Історія
Комп'ютери
Креслення
Кулінарія
Культура
Лексикологія
Література
Логіка
Маркетинг
Математика
Машинобудування
Медицина
Менеджмент
Метали і Зварювання
Механіка
Мистецтво
Музика
Населення
Освіта
Охорона безпеки життя
Охорона Праці
Педагогіка
Політика
Право
Програмування
Промисловість
Психологія
Радіо
Регилия
Соціологія
Спорт
Стандартизація
Технології
Торгівля
Туризм
Фізика
Фізіологія
Філософія
Фінанси
Хімія
Юриспунденкция
Cancer or terrorism in the body
Cancer is an abnormal growth of the body's own cells. That is, normal cells in your body decide to "mutiny" and "selfishly" take over the organ or tissue they are normally a part of, with wild uncontrolled growth. Cancer occurs when our normal cells become altered at the genetic and biochemical level in a way that permits them to divide into many more cells than would normally be present in that tissue.
Cancer is not an infectious or contagious disease like the flu, the common cold, or a bacterial infection. You can't catch it from a patient's handshake or sneeze. Cancer is really a collection of many different diseases under a single heading. Some forms of cancer, but not all, are heritable. Some, but not all, forms of cancer are caused by exposure to chemicals, or radiation, or viruses. And, different types of cancer are caused by different genetic and environmental factors.
Steps to Prevent or Reduce the Risk of Cancer:
1. Stop smoking tobacco, and avoid spending time with smokers.
2. Stop chewing tobacco.
3. Reduce exposure to CIV radiation in sunlight and tanning lamps.
4. Reduce fat in your diet.
5. Increase fiber and vegetables in diet (although this is under debate).
6. Maintain a balanced diet, including vitamins and minerals.
7. Test your basement at home for radioactive radon.
8. Reduce the number of X-rays taken by dentists and physicians
9. Avoid promiscuous sexual relations to reduce risk of viral sexually transmitted diseases. Abstain from sex or remain faithful to your spouse.
10. Avoid exposure to industrial chemicals (e.g. pesticides, insecticides, organic solvents, etc. )
UNIT-4


GENETICS
Do you look more like your father or grandfather? Do you have yourfather'seyes? What about Uncle Adam's cheekbones? Brown eyes, blue, green, or gray; black, brown, blond, or red hair-these are just a few examples of the traits that are inherited from parents. What genetic principles account for the transmission of such traits from parent to offspring? The answer is the gene.
What is genetics?
Genetics is the study of genes. In other words, it is the branch of biology that deals with the study of heredity. A gene is a segment of DMA that codes a particular trait. It is the basic unit of hereditary. Genes are located on chromosomes. They control an organism's body form and function. The different forms of a trait that a gene may have are called alleles. Some alleles can be dominant and others can be recessive. If you get a dominant gene from either of your parents, you will look more like the one from whom you received that gene.

The molecular basis of inheritance
Why was the alphabet one of the first things you learned when you started school? Letters are a code that you need to know before you learn to read.
A cell also uses a code that is stored in its hereditary material. The code is a chemical called deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA. It contains information for an organism's growth and function.
DNA is stored in cells that have a nucleus. When a cell divides, the DNA code is copied and passed to the new cells.
In this way, new cells receive the same coded information that was in the original cell. Every cell that has ever been formed in your body or in any other organism contains DNA.
| Genome sizes | ||
| Organism | Genome size | Estimated gene number |
| Human | 3200 Mb | 30.000-40.000 |
| Fruit fly | 180 Mb | |
| Yeast | 12 Mb | |
| Bacteria | 1.8 Mb | |
| Note | 1 Mb = million base |
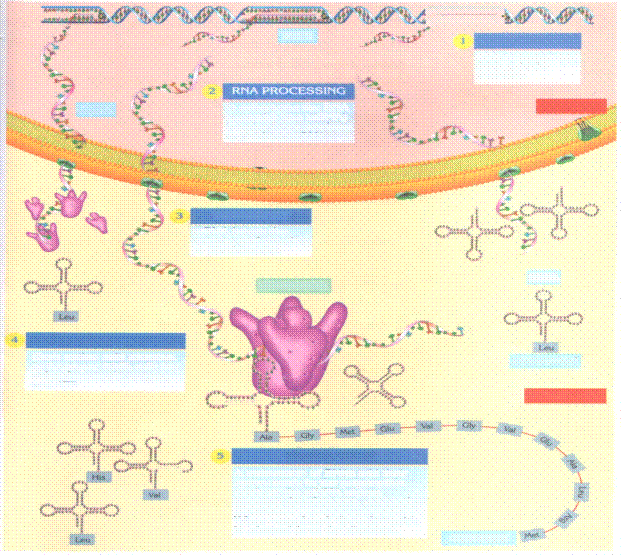
Genes in action (Protein synthesis)
Most of your characteristics, such as the color of your hair, your height, and even how things taste to you, depend on the kinds of proteins your cells make. DNA in your cells stores the instructions for making these proteins. Proteins build cells and tissues or work as enzymes. The instructions for making a specific protein are found in a gene, which is a section of DNA on a chromosome.
Each chromosome contains hundreds of genes. Proteins are made of chains of hundreds or thousands of amino acids. The gene determines the order of amino acids in a protein. Changing the order of the amino acids makes a different protein
What might occur if an important protein couldn't be made or if the wrong protein was made in your cells? Genes are found in the nucleus, but proteins are made on ribosomes in the cytoplasm. The codes for making proteins are carried from the nucleus to the ribosomes by another type of nucleic acid called ribonucleic acid, or RNA.












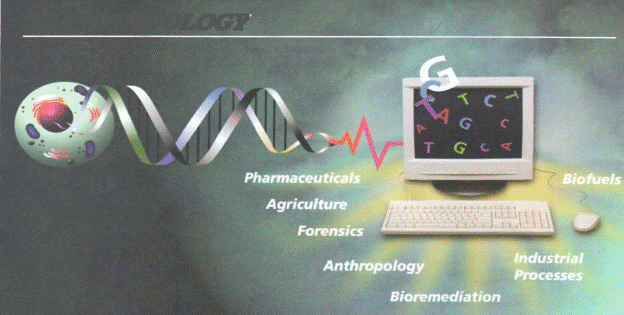
BIOTECHNOLOGY AND GENOMICS
These are new fields of biology that started in the mid 1970's. They are without doubt the most powerful tools ever developed in the field of biology, if used wisely. Genetic engineering promises to increase the quality of human life. On the other hand, if used haphazardly and carelessly, genetic engineering could have a negative effect on our quality of life.
Like any powerful tool, genetic engineering must be used carefully and wisely if we don't want unfortunate accidents. With the development of recombinant DNA and gene cloning technologies, biologists are now able to isolate and dissect essentially any gene and any segment of any chromosome of any organism. This has resulted in the explosive accumulation of new information in virtually every area of biology.
What are recombinant DNA technology and genetic engineering? They are biotechnical processes that permit the formation of new combinations of genes by isolating genes from one organism and introducing them into either a similar or an unrelated organism.
Practical applications of recombinant DNA technology
Genetic engineering holds great promise for the future. It has great potential. It is possible to isolate and dissect essentially any gene and any segment of any chromosome of any organism.
Читайте також:
- Cancer warning over stem cells
- Factors that may contribute to terrorism
- Terrorism
- Terrorism
- Transnational terrorism
- Types of Terrorism
| <== попередня сторінка | | | наступна сторінка ==> |
| Cell membrane | | | Medical and pharmaceutical applications |
|
Не знайшли потрібну інформацію? Скористайтесь пошуком google: |
© studopedia.com.ua При використанні або копіюванні матеріалів пряме посилання на сайт обов'язкове. |