
РЕЗОЛЮЦІЯ: Громадського обговорення навчальної програми статевого виховання
ЧОМУ ФОНД ОЛЕНИ ПІНЧУК І МОЗ УКРАЇНИ ПРОПАГУЮТЬ "СЕКСУАЛЬНІ УРОКИ"
ЕКЗИСТЕНЦІЙНО-ПСИХОЛОГІЧНІ ОСНОВИ ПОРУШЕННЯ СТАТЕВОЇ ІДЕНТИЧНОСТІ ПІДЛІТКІВ
Батьківський, громадянський рух в Україні закликає МОН зупинити тотальну сексуалізацію дітей і підлітків
Відкрите звернення Міністру освіти й науки України - Гриневич Лілії Михайлівні
Представництво українського жіноцтва в ООН: низький рівень культури спілкування в соціальних мережах
Гендерна антидискримінаційна експертиза може зробити нас моральними рабами
ЛІВИЙ МАРКСИЗМ У НОВИХ ПІДРУЧНИКАХ ДЛЯ ШКОЛЯРІВ
ВІДКРИТА ЗАЯВА на підтримку позиції Ганни Турчинової та права кожної людини на свободу думки, світогляду та вираження поглядів
- Гідрологія і Гідрометрія
- Господарське право
- Економіка будівництва
- Економіка природокористування
- Економічна теорія
- Земельне право
- Історія України
- Кримінально виконавче право
- Медична радіологія
- Методи аналізу
- Міжнародне приватне право
- Міжнародний маркетинг
- Основи екології
- Предмет Політологія
- Соціальне страхування
- Технічні засоби організації дорожнього руху
- Товарознавство продовольчих товарів
Тлумачний словник
Авто
Автоматизація
Архітектура
Астрономія
Аудит
Біологія
Будівництво
Бухгалтерія
Винахідництво
Виробництво
Військова справа
Генетика
Географія
Геологія
Господарство
Держава
Дім
Екологія
Економетрика
Економіка
Електроніка
Журналістика та ЗМІ
Зв'язок
Іноземні мови
Інформатика
Історія
Комп'ютери
Креслення
Кулінарія
Культура
Лексикологія
Література
Логіка
Маркетинг
Математика
Машинобудування
Медицина
Менеджмент
Метали і Зварювання
Механіка
Мистецтво
Музика
Населення
Освіта
Охорона безпеки життя
Охорона Праці
Педагогіка
Політика
Право
Програмування
Промисловість
Психологія
Радіо
Регилия
Соціологія
Спорт
Стандартизація
Технології
Торгівля
Туризм
Фізика
Фізіологія
Філософія
Фінанси
Хімія
Юриспунденкция
Price and Different Pricing Methods
Price is the monetary value that you charge to cover the cost of the product plus the other costs associated with the product, such as labor cost, promotional cost, etc., plus a profit. The decision on pricing would make or break your business. Price also conveys the message to the consumers that indicates the price-quality relationship: The higher the price, the better the quality.
 Pricing Methods
Pricing Methods
 |
| Prices are determined by the customers demand | The price is not based on production costs, but by the demand in the market. Example: For some hotels, since their main target markets are business travelers, they find it difficult to fill up their rooms during weekends. As a demand-driven pricing technique, some hotels tend to offer weekend getaway package at a special rate to fill up the hotel rooms. |
| Value pricing | It is focus on the consumer’s perception of good value for the money they pay for the product/service they receive. Example: Some people are willing to pay for $5,000 a night at a five-star hotel for the elegant lobby, the luxurious-designed room and personalized service; however, some people are only willing to pay for $500 a night at a motel or a three star hotel just for a basic, clean room. |
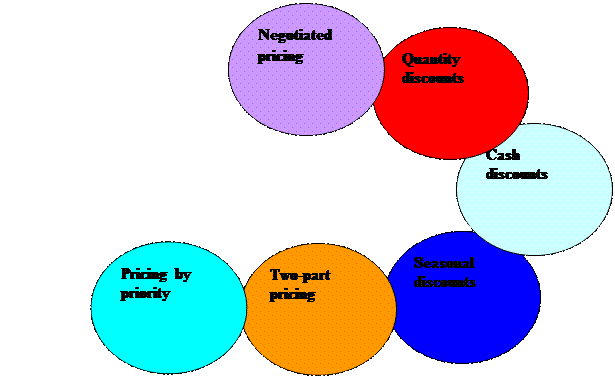
| Negotiated pricing | It is often use in the hospitality industry. Price is open for negotiation, you may not have to pay for the fixed amount given the right timing. Example: A couple plans to have their wedding banquet at a hotel. With a budget of $500 per guest, they may discuss with the caterer and negotiate for the menu items and service level they want at an agreeable price. |
| Quantity discounts | These are frequently given to customers who purchase a large amount of a product or service. Example: Each year, travel agencies will get discounts for group rates on hotel rooms, air-tickets as a promise for a pre-determined volume. |
| Cash discounts | They are given to the customers when they make a cash purchase for a product or service. The seller can use the money to invest and make money, which something the seller misses out on when allowing creditors a long time to pay. Example: In hospitality industry, suppliers often offer cash discount of up to 10% to companies for prompt payment of invoices, usually within 30 days. |
| Seasonal discounts | They are widely used by hotels, resorts and airlines, discounts are given during times when the demand is low. Example: Airlines offering off-season rates for air tickets during school year. The airfare is cheaper when compare to summer holiday where families travel with their school-aged children. |
| Two-part pricing | It is the two different components of the total price paid. Example: You have a membership for the club house of the apartment that you live. The membership fee usually consists of the initial fee as well as a fixed monthly dues to use the facilities. |
| Pricing by priority | It usually implies for those customers who are paying the most to be among the group of first priority. Examples: Airline ticket seats and concert tickets, where prices are initially high, but eventually will get lower as time approaches the take-off time or curtain time. The company would drop the prices may be considerably at the end so it can sell the remaining places or seats to last minute bargain-hunting travelers. |
| Price bundling | It is two or more products or services being combined together and sell as a package. Example: Visit Macau package is a good example: The price of the trip includes a round-trip of TurboJet, hotel accommodation, free shuttle bus to and from the hotel and free half-day tour to the local attractions. It is priced less than if they are purchased separately. |
To find the optimum pricing for your product or service is not an easy task. In addition to the material cost and other costs that associated with it, you must find a price level that the market would bear. In other words, pricing will depend on the competition and also the supply and demand situation of the market.
Читайте також:
- A DIFFERENT KIND OF EDUCATION
- ARE YOU PAYING TOO HIGH A PRICE FOR THE FUTURE?
- Article 4 Contract Price
- Cells of the cartilaginous isogenous groups that are characterized by high nucleocytoplasmic ratio. Among such cells there are many those at different stages of mitosis.
- Cheap at Half the Price
- CLINICAL METHODS OF PATIENT’S EXAMINATION
- Conversion is the main way of forming verbs in Modern English. Verbs can be formed from nouns of different semantic groups and have different meanings, e.g.
- D. Find in the text phrases containing “to get” and memorize different meanings of the verb.
- Data Collection Methods for Market Research
- Demo 11: Access Methods (методи доступу)
- Different phonological schools and their concept of phoneme
- Different Promotions Tools Associated with Push Promotions
| <== попередня сторінка | | | наступна сторінка ==> |
| Pull Promotions | | | Public Relations Means |
|
Не знайшли потрібну інформацію? Скористайтесь пошуком google: |
© studopedia.com.ua При використанні або копіюванні матеріалів пряме посилання на сайт обов'язкове. |