
РЕЗОЛЮЦІЯ: Громадського обговорення навчальної програми статевого виховання
ЧОМУ ФОНД ОЛЕНИ ПІНЧУК І МОЗ УКРАЇНИ ПРОПАГУЮТЬ "СЕКСУАЛЬНІ УРОКИ"
ЕКЗИСТЕНЦІЙНО-ПСИХОЛОГІЧНІ ОСНОВИ ПОРУШЕННЯ СТАТЕВОЇ ІДЕНТИЧНОСТІ ПІДЛІТКІВ
Батьківський, громадянський рух в Україні закликає МОН зупинити тотальну сексуалізацію дітей і підлітків
Відкрите звернення Міністру освіти й науки України - Гриневич Лілії Михайлівні
Представництво українського жіноцтва в ООН: низький рівень культури спілкування в соціальних мережах
Гендерна антидискримінаційна експертиза може зробити нас моральними рабами
ЛІВИЙ МАРКСИЗМ У НОВИХ ПІДРУЧНИКАХ ДЛЯ ШКОЛЯРІВ
ВІДКРИТА ЗАЯВА на підтримку позиції Ганни Турчинової та права кожної людини на свободу думки, світогляду та вираження поглядів
- Гідрологія і Гідрометрія
- Господарське право
- Економіка будівництва
- Економіка природокористування
- Економічна теорія
- Земельне право
- Історія України
- Кримінально виконавче право
- Медична радіологія
- Методи аналізу
- Міжнародне приватне право
- Міжнародний маркетинг
- Основи екології
- Предмет Політологія
- Соціальне страхування
- Технічні засоби організації дорожнього руху
- Товарознавство продовольчих товарів
Тлумачний словник
Авто
Автоматизація
Архітектура
Астрономія
Аудит
Біологія
Будівництво
Бухгалтерія
Винахідництво
Виробництво
Військова справа
Генетика
Географія
Геологія
Господарство
Держава
Дім
Екологія
Економетрика
Економіка
Електроніка
Журналістика та ЗМІ
Зв'язок
Іноземні мови
Інформатика
Історія
Комп'ютери
Креслення
Кулінарія
Культура
Лексикологія
Література
Логіка
Маркетинг
Математика
Машинобудування
Медицина
Менеджмент
Метали і Зварювання
Механіка
Мистецтво
Музика
Населення
Освіта
Охорона безпеки життя
Охорона Праці
Педагогіка
Політика
Право
Програмування
Промисловість
Психологія
Радіо
Регилия
Соціологія
Спорт
Стандартизація
Технології
Торгівля
Туризм
Фізика
Фізіологія
Філософія
Фінанси
Хімія
Юриспунденкция
Численные методы решения уравнения адвекции
The basic idea behind Finite-difference, grid-based methods is to slap a static grid over the solution space and to approximate the partial differentials at each point in the grid. The standard approach for approximating the differentials comes from truncated Taylors series. Consider a function f(x, t) at a fixed time t. If f is continuous in space we can expand it around any point f(x + _x) as

where the subscripted x imply partial differentiation with respect to x. If we ignore terms in this series of order _x2 and higher we could approximate the first derivative at any point x0 as

If we consider our function is now stored in a discrete array of points fj and x = _xj where _x is the grid spacing, then at time step n we can write the forward space or FS derivative as

An identical procedure but expanding in time gives the forward time derivative (FT) as
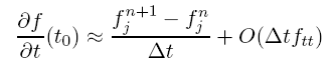
Both of these approximations however are only first order accurate as the leading term in the truncation error is of order _x or _t. More importantly, this approximation will only be exact for piecewise linear functions where fxx or ftt = 0.
Other combinations and higher order schemesIn Eq. (5.3.1) we considered the value of our function at one grid point forward in _x. We could just have easily taken a step backwards to get

If we truncate at order _x2 and above we still get a first order approximation for the Backward space step (BS)
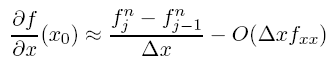
which isn’t really any better than the forward step as it has the same order error (but of opposite sign). We can do a fair bit better however if we combine Eqs. (5.3.1) and (5.3.5) to remove the equal but opposite 2nd order terms. If we subtract (5.3.5) from (5.3.1) and rearrange, we can get the centered space (CS) approximation
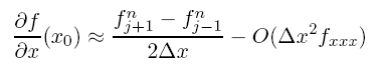
Note we have still only used two grid points to approximate the derivative but have gained an order in the truncation error. By including more and more neighboring points, even higher order schemes can be dreamt up (much like the 4th order Runge Kutta ODE scheme), however, the problem of dealing with large patches of points can become bothersome, particularly at boundaries. By the way, we don’t have to stop at the first derivative but we can also come up with approximations for the second derivative (which we will need shortly). This time, by adding (5.3.1) and (5.3.5) and rearranging we get

This form only needs a point and its two nearest neighbours. Note that while the truncation error is of order _x2 it is actually a 3rd order scheme because a cubic polynomial would satisfy it exactly (i.e. fxxxx = 0).
Направленная вперед по времени центральная по пространству схема
I will show you a simple, easily coded and totally unstable technique known as forward-time centered space or simply the FTCS method. If we consider the canonical 1-D transport equation with constant velocities (5.2.2) and replace the time derivative with a FT approximation and the space derivative as a CS approximation we can write the finite difference approximation as

or rearranging for cn+1 j we get the simple updating scheme

where

is the Courant number which is simply the number of grid points traveled in a single time step.
Читайте також:
- IX. Уравнения параболического типа
- VII. Нахождение общего решения методом характеристик
- X. Уравнения эллиптического типа
- Еще одна форма записи уравнения динамики вращательного движения
- Методы очистки сточных вод.
- Методы теоретического и эмпирического уровней научного познания
- Отдельные представители. Методы идентификации.
- Социально-экономические и экологические проблемы регионов и пути их решения
- ТЕМА 1.5. МЕТОДЫ ОРГАНИЗАЦИИ НЕПОТОЧНОГО ПРОИЗВОДСТВА
- Тема 2. БИОСИСТЕМЫ, ОБЪЕКТЫ И МЕТОДЫ В
- Тема 6. Методы анализа и прогнозирования развития среды организации
- Уравнения прямой, проходящей через две точки
| <== попередня сторінка | | | наступна сторінка ==> |
| Питання, які підлягають вирішенню при дослідженні крові, волосся, сперми та інших виділень організму людини. | | |
|
Не знайшли потрібну інформацію? Скористайтесь пошуком google: |
© studopedia.com.ua При використанні або копіюванні матеріалів пряме посилання на сайт обов'язкове. |