
МАРК РЕГНЕРУС ДОСЛІДЖЕННЯ: Наскільки відрізняються діти, які виросли в одностатевих союзах
РЕЗОЛЮЦІЯ: Громадського обговорення навчальної програми статевого виховання
ЧОМУ ФОНД ОЛЕНИ ПІНЧУК І МОЗ УКРАЇНИ ПРОПАГУЮТЬ "СЕКСУАЛЬНІ УРОКИ"
ЕКЗИСТЕНЦІЙНО-ПСИХОЛОГІЧНІ ОСНОВИ ПОРУШЕННЯ СТАТЕВОЇ ІДЕНТИЧНОСТІ ПІДЛІТКІВ
Батьківський, громадянський рух в Україні закликає МОН зупинити тотальну сексуалізацію дітей і підлітків
Відкрите звернення Міністру освіти й науки України - Гриневич Лілії Михайлівні
Представництво українського жіноцтва в ООН: низький рівень культури спілкування в соціальних мережах
Гендерна антидискримінаційна експертиза може зробити нас моральними рабами
ЛІВИЙ МАРКСИЗМ У НОВИХ ПІДРУЧНИКАХ ДЛЯ ШКОЛЯРІВ
ВІДКРИТА ЗАЯВА на підтримку позиції Ганни Турчинової та права кожної людини на свободу думки, світогляду та вираження поглядів
РЕЗОЛЮЦІЯ: Громадського обговорення навчальної програми статевого виховання
ЧОМУ ФОНД ОЛЕНИ ПІНЧУК І МОЗ УКРАЇНИ ПРОПАГУЮТЬ "СЕКСУАЛЬНІ УРОКИ"
ЕКЗИСТЕНЦІЙНО-ПСИХОЛОГІЧНІ ОСНОВИ ПОРУШЕННЯ СТАТЕВОЇ ІДЕНТИЧНОСТІ ПІДЛІТКІВ
Батьківський, громадянський рух в Україні закликає МОН зупинити тотальну сексуалізацію дітей і підлітків
Відкрите звернення Міністру освіти й науки України - Гриневич Лілії Михайлівні
Представництво українського жіноцтва в ООН: низький рівень культури спілкування в соціальних мережах
Гендерна антидискримінаційна експертиза може зробити нас моральними рабами
ЛІВИЙ МАРКСИЗМ У НОВИХ ПІДРУЧНИКАХ ДЛЯ ШКОЛЯРІВ
ВІДКРИТА ЗАЯВА на підтримку позиції Ганни Турчинової та права кожної людини на свободу думки, світогляду та вираження поглядів
Контакти
- Гідрологія і Гідрометрія
- Господарське право
- Економіка будівництва
- Економіка природокористування
- Економічна теорія
- Земельне право
- Історія України
- Кримінально виконавче право
- Медична радіологія
- Методи аналізу
- Міжнародне приватне право
- Міжнародний маркетинг
- Основи екології
- Предмет Політологія
- Соціальне страхування
- Технічні засоби організації дорожнього руху
- Товарознавство продовольчих товарів
Тлумачний словник
Авто
Автоматизація
Архітектура
Астрономія
Аудит
Біологія
Будівництво
Бухгалтерія
Винахідництво
Виробництво
Військова справа
Генетика
Географія
Геологія
Господарство
Держава
Дім
Екологія
Економетрика
Економіка
Електроніка
Журналістика та ЗМІ
Зв'язок
Іноземні мови
Інформатика
Історія
Комп'ютери
Креслення
Кулінарія
Культура
Лексикологія
Література
Логіка
Маркетинг
Математика
Машинобудування
Медицина
Менеджмент
Метали і Зварювання
Механіка
Мистецтво
Музика
Населення
Освіта
Охорона безпеки життя
Охорона Праці
Педагогіка
Політика
Право
Програмування
Промисловість
Психологія
Радіо
Регилия
Соціологія
Спорт
Стандартизація
Технології
Торгівля
Туризм
Фізика
Фізіологія
Філософія
Фінанси
Хімія
Юриспунденкция
Ex. 2.Use the words from the previous exercise to fill in the gaps below
1 Company ----------- are often much too optimistic, and make unrealistically high--------------------______________________________
2 If a start-up's---------------- doesn't appear to be------------------, e.g. because of the threat of new entrants, investors won't be interested.
3. It took three years for our-----------------to reach our------------- -----------------, but in the fourth year we finally made a profit.
4.Big companies sometimes lose some of their best------------------ to start-ups, and
this can happen to start-ups too once they have become established.
5.An investor's---------------------can be sabotaged by events such as a suddenly falling stock market.
Ex.3 Role play: Investing in start-ups
Imagine that you are investment managers for a large financial institution such as a pension fund or an insurance company that has decided to invest up to 2% of its assets in start-up companies.
It will not be difficult to find companies in which to invest, because you regularly receive propositions from venture capital firms. But first, you want to establish a strategy. Which industries or industry sectors do you think you should invest in? Which industries have the most potential? Which industries or technologies probably present the fewest risks? If you are going to invest in companies in your own country, in which industries does it have expertise or a competitive advantage?
|
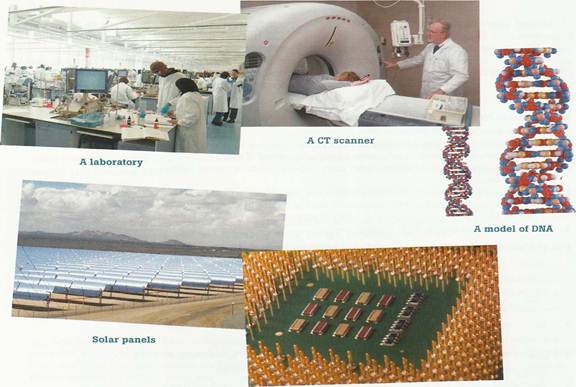
Choose three of the sectors listed below. Prepare a short presentation of your strategy in small groups. Then change groups and explain your strategy to your colleagues, and then present your decisions to the class.
A microprocessor
• computer and video game technology
• DNA sequencing and genetic medicine
• fuel-efficient aeroplane (BrE) or airplane (AmE) technology
• genetically modified food
• high-speed rail transport
• hybrid (petrol and electric battery) automobile technology
• microprocessors using nanotechnology
• mobile telephone technology
• nuclear energy
• nuclear medical imaging
• solar energy technology
• wind energy technology
• other?
Читайте також:
- A) COLLOQUIAL WORDS
- A) Match the words on the left with the expressions on the right.
- A) Match the words to make word combinations
- A) Practise using the words and word combinations in bold type to make other comparisons between some two-four regions of Russia. Write your best sentences down.
- A) Read the words describing the qualities required for the legal profession and translate them into Russian. Use a dictionary.
- A) Scan the text and fill in the table below.
- A. Make up short dialogues expressing your opinion, agreeing or disagreeing. Use the prompts given below.
- A. Sarah and Ken are having an argument. Read what Sarah says and complete the dialogue with Ken’s answers from the box below. Then try to guess his last answer.
- A. The adjectives below can be used to describe inventions or new ideas. Which have a positive meaning? Which have a negative meaning?
- Additional Exercise
- Analyze the meanings of the italicized words. Identify the result of the changes of the connotational aspect of lexical meaning in the given words.
- And write your own sentences with the same words and phrases.
| <== попередня сторінка | | | наступна сторінка ==> |
| VOCABULARY | | | Ex.4 Writing |
|
Не знайшли потрібну інформацію? Скористайтесь пошуком google: |
© studopedia.com.ua При використанні або копіюванні матеріалів пряме посилання на сайт обов'язкове. |