
РЕЗОЛЮЦІЯ: Громадського обговорення навчальної програми статевого виховання
ЧОМУ ФОНД ОЛЕНИ ПІНЧУК І МОЗ УКРАЇНИ ПРОПАГУЮТЬ "СЕКСУАЛЬНІ УРОКИ"
ЕКЗИСТЕНЦІЙНО-ПСИХОЛОГІЧНІ ОСНОВИ ПОРУШЕННЯ СТАТЕВОЇ ІДЕНТИЧНОСТІ ПІДЛІТКІВ
Батьківський, громадянський рух в Україні закликає МОН зупинити тотальну сексуалізацію дітей і підлітків
Відкрите звернення Міністру освіти й науки України - Гриневич Лілії Михайлівні
Представництво українського жіноцтва в ООН: низький рівень культури спілкування в соціальних мережах
Гендерна антидискримінаційна експертиза може зробити нас моральними рабами
ЛІВИЙ МАРКСИЗМ У НОВИХ ПІДРУЧНИКАХ ДЛЯ ШКОЛЯРІВ
ВІДКРИТА ЗАЯВА на підтримку позиції Ганни Турчинової та права кожної людини на свободу думки, світогляду та вираження поглядів
- Гідрологія і Гідрометрія
- Господарське право
- Економіка будівництва
- Економіка природокористування
- Економічна теорія
- Земельне право
- Історія України
- Кримінально виконавче право
- Медична радіологія
- Методи аналізу
- Міжнародне приватне право
- Міжнародний маркетинг
- Основи екології
- Предмет Політологія
- Соціальне страхування
- Технічні засоби організації дорожнього руху
- Товарознавство продовольчих товарів
Тлумачний словник
Авто
Автоматизація
Архітектура
Астрономія
Аудит
Біологія
Будівництво
Бухгалтерія
Винахідництво
Виробництво
Військова справа
Генетика
Географія
Геологія
Господарство
Держава
Дім
Екологія
Економетрика
Економіка
Електроніка
Журналістика та ЗМІ
Зв'язок
Іноземні мови
Інформатика
Історія
Комп'ютери
Креслення
Кулінарія
Культура
Лексикологія
Література
Логіка
Маркетинг
Математика
Машинобудування
Медицина
Менеджмент
Метали і Зварювання
Механіка
Мистецтво
Музика
Населення
Освіта
Охорона безпеки життя
Охорона Праці
Педагогіка
Політика
Право
Програмування
Промисловість
Психологія
Радіо
Регилия
Соціологія
Спорт
Стандартизація
Технології
Торгівля
Туризм
Фізика
Фізіологія
Філософія
Фінанси
Хімія
Юриспунденкция
Types of meaning.
DOVE
BASIC NOTIONS OF THE LECTURE.
Semasiology - is the branch of linguistics that is devoted to the study of meaning.
Meaning – is a certain reflection in our mind of objects, phenomena or relations, which makes inner-faced part of linguistic sign, the sound form functions as its out-faced part.
There are 2 approaches to meaning.
1. Referential – formulates the essence of meaning by establishing the dependence between words and things and concepts they denote.
2. Functional – studies functions of the word in speech, less concerned with what meaning is, rather with how it works.
All works on the theory of meaning are based on referential approach. The essential feature of this approach is that it distinguishes between 3 components, closely connected with meaning:
· The sound form of the sign
· The concept, underlining this sound form
· The actual referent – aspect of reality to which the linguistic sign refers.
The referential model of meaning is called “basic triangle”. It underlines the semantic system of all principles of this school.


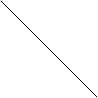 Concept (bird)
Concept (bird)
Sound form Referent (a particular bird – голуб)
Sound form of the linguistic sign “dove” is connected with our concept of the bird, which denotes the actual referent.
So, the common feature of referential approach is implication that meaning is in some case connected with the referent.
Functional approach claims that a linguistic study of meaning is the investigation of the relation of sign to sign only. The meaning of linguistic units may be studied through their relation to other linguistic units, not through relation to concept or referent.
So, meanings of words “move” and “movement” are different because they function in speech differently.
1. Grammatical – is a component of meaning, recurrent in identical sets of individual forms of words (e.g. plural of nouns, Past Indefinite etc.).
2. Lexical meaning has denotational and connotational components.
The denotational component expresses notional content of a word and makes communication possible.
Denotation – expression of main meaning, meaning proper of a linguistic unit, in contrast to its connotation.
Connotational component – additional semantic meaning.
Types of connotation:
· Emotive
· Evaluative
· Connotation of duration and cause.
Connotation – supplementary meaning and stylistic shade that is added to the word’s main meaning and express all sorts of emotional, expressive overtones.
A word having several meanings is called polysemantic.
The ability of words to have more than one meaning is named polysemy.
The system of meanings of every polysemantic word develops gradually, over the centuries. As more meanings are added, some of old meanings may be lost.
There are 2 levels of analysis of semantic structure of polysemantic words.
1. The semantic structure of a word is treated as the system of meanings.
E.g.: fire – 1) flame (полум’я)
2) an instance of destructive burning (пожежа)
3) burning material in the stove, fireplace (вогонь)
4) the shooting of guns (артилерійський вогонь)
5) strong feeling, passion
6) strong pain.
Meaning 1 is a dominant, describes concept in the most general way, other meanings are associated with special aspects of the same phenomenon. Meaning 1 is a centre of semantic structure and is the main meaning. Meanings 2-6 are secondary meanings and can be associated with one another.
2. Each meaning can be divided into semantic components.
Читайте також:
- Classification of phraseological units and their structural types.
- Grammatical meaning.
- Grammatical meaning.
- Lesson 30 Types of Combat
- Look at this form of a music collection. Label the data types with words from B opposite.
- Replacements of sentence types
- The Types of Managers
- Types of dictionaries
- TYPES OF FICTIONAL TIME
- Types of Fitness Programs
- Types of Fitness Programs
| <== попередня сторінка | | | наступна сторінка ==> |
| Мережні сервіси (служби) і застосування | | | Transference (metaphor and metonymy). |
|
Не знайшли потрібну інформацію? Скористайтесь пошуком google: |
© studopedia.com.ua При використанні або копіюванні матеріалів пряме посилання на сайт обов'язкове. |